How On-Device AI Is Powering the Next Generation of iOS Apps
In 2026, on device AI isn’t a futuristic concept – it brings tangible, measurable value, transforming app experiences across industries. Below are some recognizable examples showing real-time Apple intelligence in action.
Healthcare and Wellness
On device AI in iOS enables health apps and third-party fitness trackers to securely process sensitive user data, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, or activity levels, directly on the user’s device.
Apple Health utilizes local models to detect health patterns, suggest wellness insights, and monitor irregularities without sending private information to external servers.
Apple Watch analyzes motion, heart rate, and ECG data on-device to detect irregular rhythms, falls, or exercise patterns in real time. Meanwhile, ML models run locally to send instant notifications, even without an internet connection.
Fintech and Banking
On-device AI can ensure both privacy and instant responses, which are crucial for activities related to finances.
Apple Pay and Wallet use local AI for biometric authentication (Face ID, Touch ID) and fraud detection, ensuring data never leaves the device.
E-Learning
Education apps powered by on-device AI can introduce exceptional personalization, adapting to user behavior in real time, even offline.
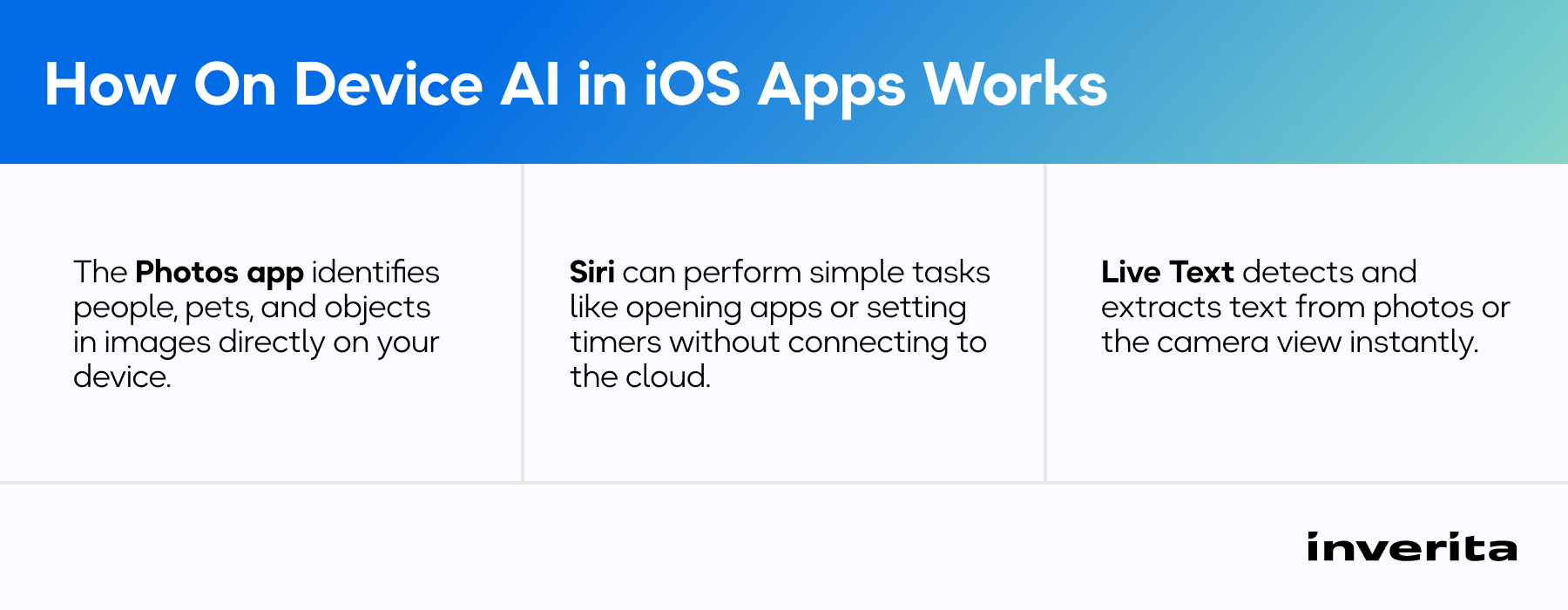
With Apple on device LLMs, apps like Notes and Freeform can understand handwriting, summarize content, and reorganize written materials using on-device language models.
Apple’s native Writing Tools can proofread selected text, rewrite in a different tone or style, summarise or extract key points, and convert to lists or tables – all with the help of Apple on device LLM.
Media and Creativity
Apple taps into the power of local intelligence to unlock new creativity opportunities, enabling instant content editing with high-quality results and no lag, regardless of network connectivity.
Apple Photos uses on-device computer vision to recognize faces, categorize objects, and generate personalized “Memories” collections. It also leverages AI to analyze and automatically tag the content of all photos (people, places, objects, scenes), making it possible to search through the entire library using natural language terms.
Apple's Camera heavily relies on on-device iOS AI using its custom-designed Neural Engine and the Core ML framework to deliver advanced photographic capabilities:
- Deep Fusion – captures up to nine images, which are then analyzed by the Neural Engine to merge the best parts of each, resulting in a single photo with superior detail, texture, and reduced noise.
- Smart HDR – the AI system identifies different objects and areas within the scene and applies separate, optimal exposure and processing settings to each one.
- Night Mode – the camera snaps many pictures quickly, and the on-device AI aligns them, corrects for motion, and intelligently fuses them to produce a brighter, more detailed image.
- Portrait Mode and Cinematic Mode – AI algorithms do semantic segmentation and depth mapping to separate the main subject from the background accurately.
- Photographic Styles – AI performs local edits to a photo based on a chosen style, ensuring a personalized yet natural result.
- Scene Recognition – the camera automatically identifies the subject (e.g., food, landscape, person, pet) and instantly optimizes settings like color, contrast, and exposure.
Keynote and Pages feature Image Playground, allowing users to quickly generate unique images (in styles like Animation, Illustration, or Sketch) based on a text description, which can then be dropped directly into the document or presentation.
Communication Apps
The most common uses for on device AI in iOS are integrated directly into one’s keyboard and messaging experience:
- Predictive text and auto-correction.
- Converting speech to text in real-time with AI adapting to a user’s voice, accent, and vocabulary over time, significantly increasing accuracy and speed.
- Contextually appropriate smart reply suggestions and message summaries.
In apps like Messages, FaceTime, and Phone, the on-device translation model processes text and speech to provide live translated captions or spoken translations without relying on a cloud server, ensuring the privacy of your conversations.
Navigation
Apple Maps uses AI and ML to blend data from multiple sources, therefore improving accuracy, safety, and delivering smarter, more adaptive navigation experiences.
By analyzing individual travel habits and real-time traffic data, it can offer predictive destination suggestions, optimize routes on the go, and automatically adjust directions to avoid congestion or delays. AI also enhances search capabilities, helping users find places even from incomplete or vague queries. Altogether, the on device AI for iOS turns Apple Maps from a navigation app into an intelligent travel assistant that anticipates user needs and provides personalized guidance.
Challenges Developers Face When Building with On Device AI
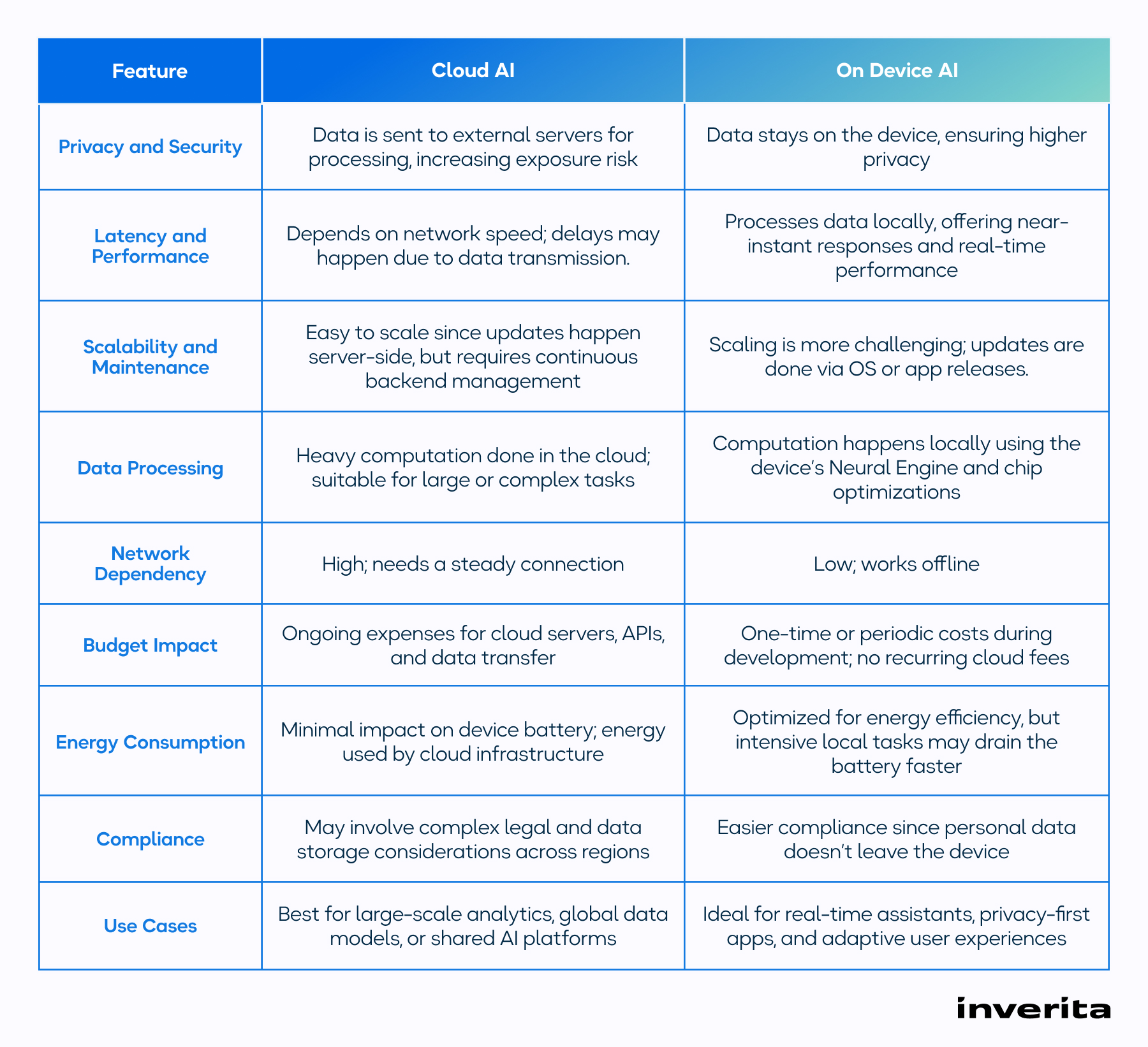
While on device AI brings attractive bonuses such as high speed, privacy, and autonomy, developers deal with trade-offs when building and deploying intelligent apps on iOS devices.
Hardware and Memory Constraints
Unlike cloud infrastructure, iPhones and iPads have limited CPU, GPU, and storage capacity, requiring developers to optimize models carefully – ensuring smooth performance without overheating devices or draining battery life.
Data Privacy and Model Training Needs
On-device AI keeps user data private, limiting access to large-scale centralized datasets needed for model improvement. Developers have to turn to federated learning or incremental on device training to bridge this gap.
Model Size and Accuracy
To enable models to run locally, developers must use techniques like pruning, quantization, and compression, but over-optimization can compromise accuracy. Finding the right balance is a constant trade-off.
Compatibility Across Devices
Ensuring consistent AI performance across Apple’s entire ecosystem – from older iPhones to the latest M-series devices – can be challenging.
Development Complexity and Talent Gap
Building apps with on-device intelligence requires a mix of specialized skills – from machine learning and Core ML integration to hardware-level optimization. Many teams underestimate this learning curve, leading to higher costs and longer timelines.
Testing and Debugging Limitations
Testing AI behavior in real-world, decentralized environments is harder than in cloud AI, where centralized monitoring is much easier.
Compliance and Data Governance
Even though data stays local, on device AI still raises compliance concerns – including user consent, federated data management, and transparency in model updates.
Maintenance and Model Updates
Unlike cloud models that update centrally, on device AI requires pushing updates to millions of devices individually.
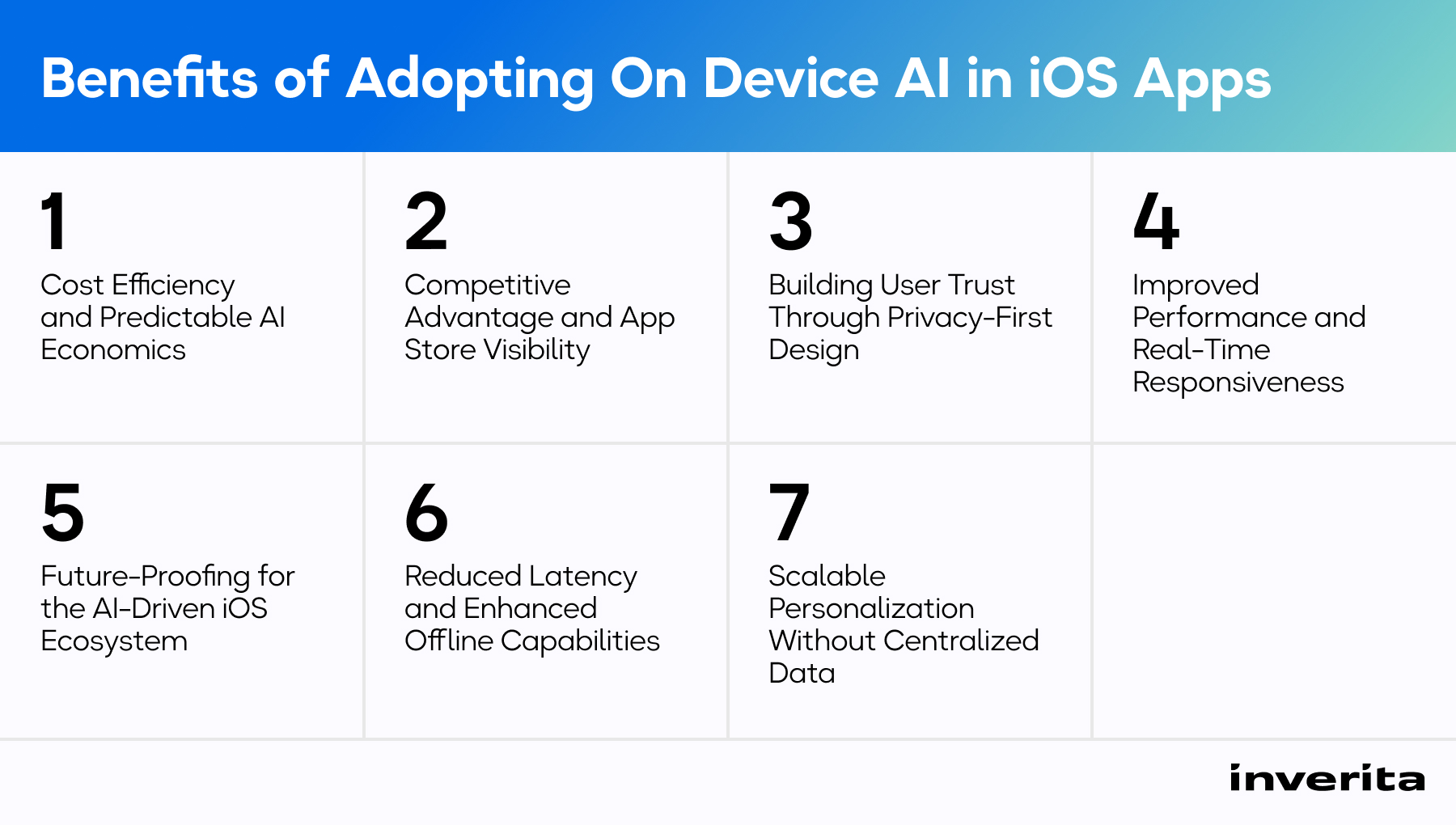
Why Now Is the Time to Adopt On Device AI in iOS Apps