Slack’s Data Usage for AI Training
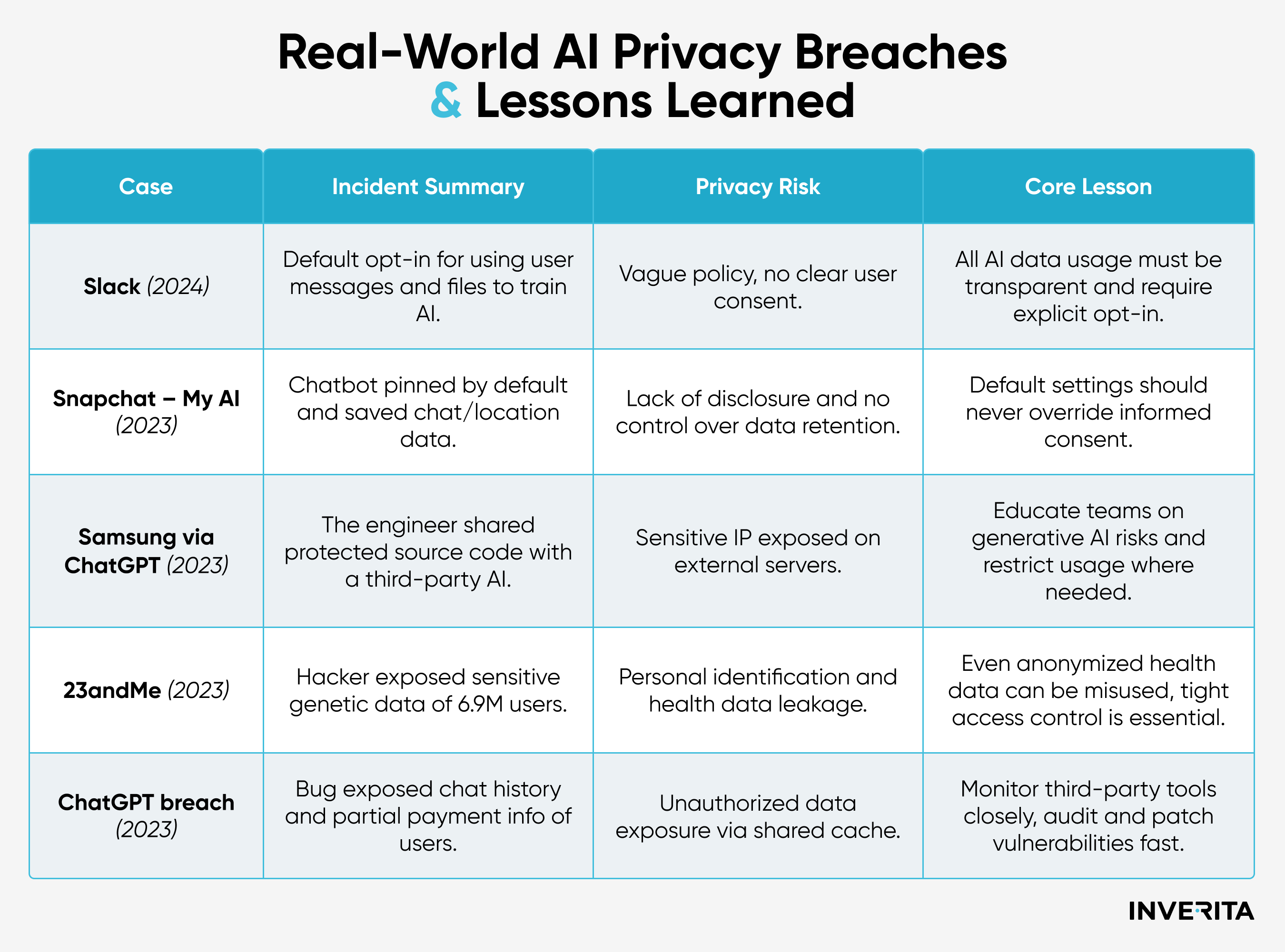
In 2024, Slack was heavily criticized after updating its privacy policy that allowed user messages and files to be used, by default, to train its AI models unless workspace administrators opted out. Although Slack clarified that its new generative AI model didn’t use customer data, the controversy showed how vague policies and default opt-in settings can drive strong backlash and erode user trust.
Snapchat's “My AI” Chatbot Privacy Concerns
In 2023, Snapchat faced backlash after launching its My AI chatbot, which was pinned by default in user chats and stored interactions for improvement. Users were not clearly informed that their messages and potentially location data could be saved, raising concerns about transparency and data security during social media activities. While Snapchat later added clearer disclosures and opt-out options, the case highlighted the risks of using generative AI without proper consent and controls.
Samsung Data Leak via ChatGPT
In 2023, Samsung banned employee use of ChatGPT and other generative AI tools after an engineer accidentally uploaded sensitive source code to the platform. The company raised concerns that data shared with AI chatbots was stored on third-party servers owned by companies operating the service, like OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google, with no easy way to retrieve or delete it. Samsung also claimed that the sensitive data could potentially be exposed to other users.
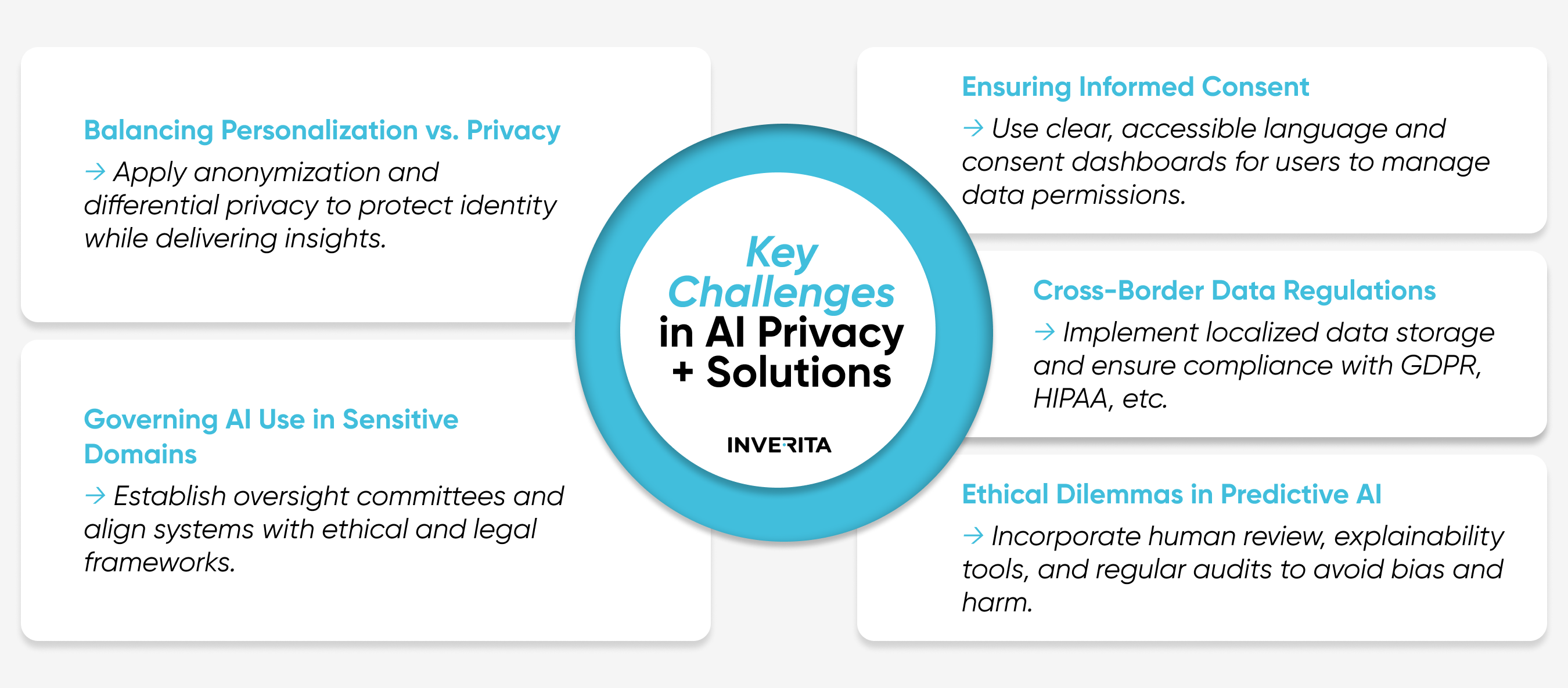
Practical Solutions to AI Privacy Risks
Ensuring accountable, secure implementation and proactively addressing potential security issues related to AI use in business environments is necessary to safeguard reputation. For this, companies should adopt the following strategies and embed privacy into the system’s design and architecture.
Implementing Privacy by Design
Consider AI privacy as a fundamental system design principle, not just a policy. This means integrating robust data protection into the development lifecycle – from data collection and preparation to model training and implementation.
Data Minimization and Anonymization
This strategy involves collecting only the data required for a particular task, ensuring explicit, informed consent from users to use their personal information in specified ways. To prevent user profiling, companies should implement techniques like data masking, tokenization, or differential privacy for anonymization.
Interpretable and Explainable AI
Interpretable and explainable AI methods provide a better understanding of how smart algorithms make decisions by breaking down and analyzing outcome patterns. This transparency reduces the risks associated with “black box” models by revealing the reasoning behind predictions or actions, making it easier to identify biases or mistakes.
How inVerita Helps You Build Ethical and Private AI Solutions
At inVerita, we provide expert AI software development services across diverse industries, including those highly regulated like healthcare and fintech. We design our AI solutions to comply with strict data security regulations. By implementing advanced encryption, data tokenization, and compliance protocols, we ensure that sensitive information of your organization and your customers is well protected.
Whether you need expert consulting, custom AI development, integration, or optimization services, our team of seasoned AI engineers and data scientists is ready to deliver the best-fitting solution with data privacy principles embedded into it.
Future of AI Privacy: What Lies Ahead
AI isn’t just a buzzword or a brief trend this technology will continue to redefine industries, integrating deeper into our daily life. As it continues to evolve and expand, concerns around data privacy will only grow more urgent. Ensuring data security in AI will require both innovative technologies and forward-thinking governance.
Take a look at some of the best emerging trends expected to drive stronger data protection in the age of AI.
The Role of Quantum-Proof Encryption
As quantum computing advances, traditional encryption methods may become vulnerable to decryption, posing a serious risk to AI systems that rely on encrypted data. Quantum-proof encryption refers to cryptographic algorithms designed to withstand quantum computing attacks, ensuring the protection of sensitive data used in AI models.
Rise of Decentralised AI Technologies
The rise of blockchain technology triggered new opportunities in decentralised AI technology as a foundation for robust privacy and security. Instead of relying on a single server, decentralised AI systems distribute model training and processing across a network of devices, keeping sensitive data closer to its source. By reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure, decentralised AI offers stronger data protection, minimizing risks of breaches and unauthorized access.
Consumer Awareness and Digital Rights
Security measures and regulatory compliance are critical, yet data privacy also depends on individuals sharing their information with AI. With growing data protection concerns, users are becoming more aware of how their data is collected, shared, and used, more mindful about their online activities, and are beginning to demand greater transparency and control. Widely available tools like privacy settings, ad opt-outs, and data access requests help users maintain control of their personal information.
Final Thoughts
As AI becomes a fundamental technology, expanding its impact across industries, addressing data security challenges becomes paramount as well. Privacy isn’t a trade-off for using AI, it’s a requirement for earning and maintaining trust.
Organizations, adopting smart algorithms, should take a multifaceted approach involving technological and regulatory solutions as well as cooperation between diverse stakeholders.
Those that view AI privacy not as a limitation, but as a competitive edge, integrating ethical data practices, fostering trust across operations, and demanding accountability at every level,will be able to tap into the AI’s full power without compromising on individual privacy rights.
Don’t hesitate to contact us if you need expert help with integrating AI securely in your business, or enhancing its capabilities and use. 

_1754038633.png)