The old saying goes, time is money. While some time ago, embedding technology in the warehouse was a privilege of big companies, today small businesses can also afford innovation. The future of warehousing is automation. Every savvy business is looking for new ways to transform the supply chain, reinforce asset utilization, and boost productivity.
What is automated warehouse that will streamline the fulfillment handle, minimize the labor-intensive processes, improve accuracy, and help your business attain solid ROI?
What is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation is the process of application of specialized storage, equipment, and retrieval systems to eliminate or minimize the labor-intensive processes that require repetitive physical tasks, human-held data entry, analysis, etc.
How automation works?
For example, in Alibaba warehouses, 70% of processes are held by robots. They are able to pick and carry up to 500 kilograms at once, moving inventory from one part of the warehouse to another, or to the shipping zone, updating all the warehouse records automatically. What is more, the robots are equipped with special sensors not to collide with each other and are able to recharge themselves by going to the nearest charging station so they don’t need any human assistance.
However, it’s a common misconception to answer “robots” to the “what is automated warehouse” question. Automated warehouse meaning goes far beyond robotics.
Automation in warehousing doesn’t necessarily require robotics or physical automation of warehouse. In many cases, automated warehouses just implement software to substitute manual tasks and improve the efficiency and accuracy of processes.
What is Digital Automation?
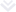
Digital automation in warehouse leverages software and gathered and thoroughly analyzed data to automate repetitive and strenuous tasks, boost productivity, and increase the safety and efficiency of operations. Let’s have a look at some of the digital warehouse automation examples.
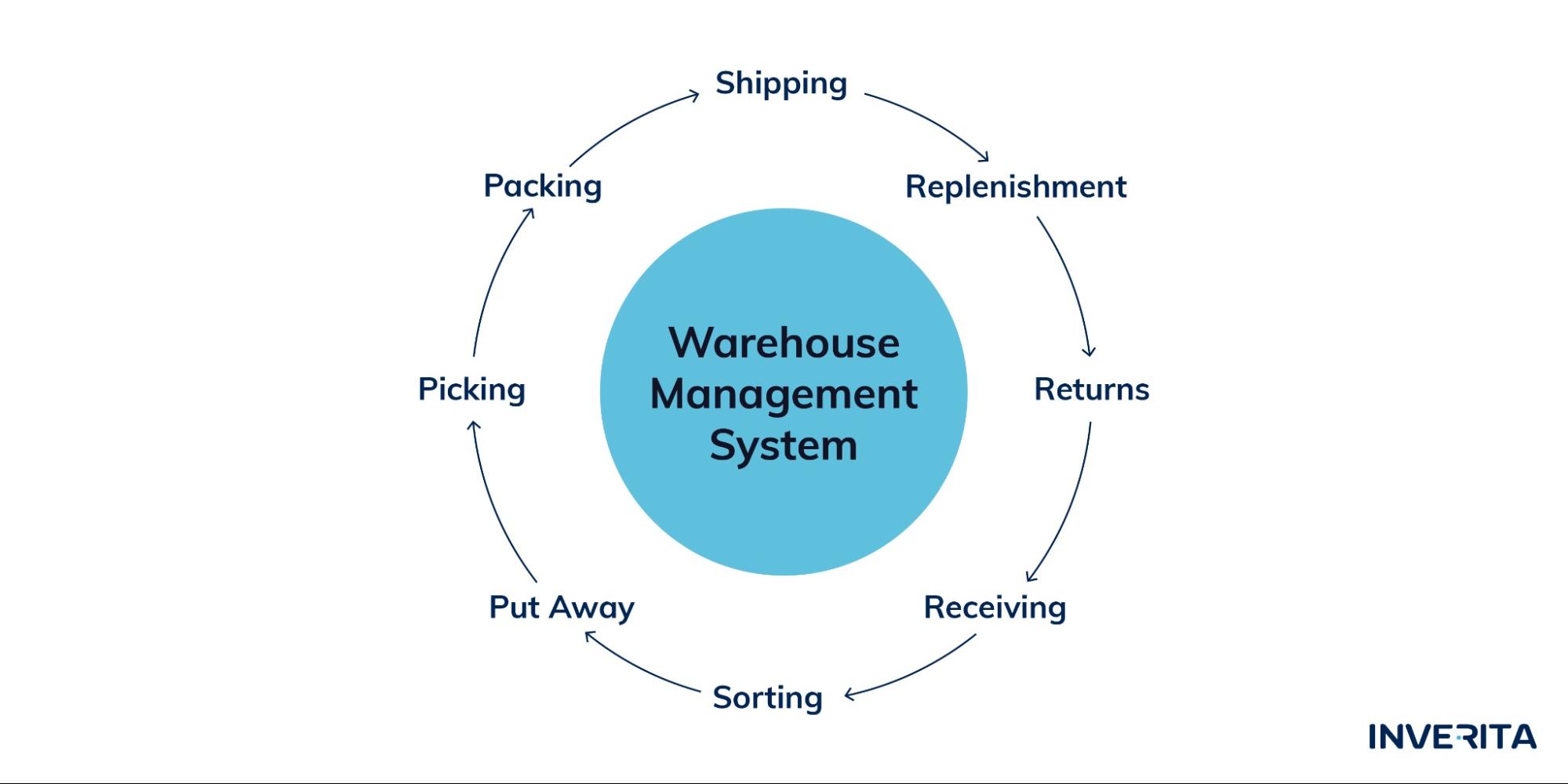
Warehouse Management Software
A WMS is a software application that enables centralized task management. Such an app assists with inventory control to optimize space inside the warehouse, provides visibility of real-time inventory levels, assigns tasks in the most efficient way, processes orders, and ensures timely delivery of products.
The number of functions and the complexity of the WMS may vary depending on the needs and budget of the business.
Handheld Terminals
HHT is used for quick and effective data access, barcode scanning, and instant information updating. In the past, this device was used primarily by large companies though now it’s widely used in warehouses of different sizes due to its reasonable price and broad functionality.
ML Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are very broadly used in what are automated warehouses today. They enable warehouse bots to choose the best picking and slotting routes, pick up the proper type of packaging depending on the size, weight, and shape of the item, generate and analyze large piles of unstructured data, make predictions about customer demand, delivery time, monitors the employees’ individual performance, accuracy, and much more.
What is Physical Automation in the Warehouse?
Warehouse physical automation is the process of improving workflows by minimizing employees’ physical activity. Robotic automation is one of the examples of physical automation in the warehouse.
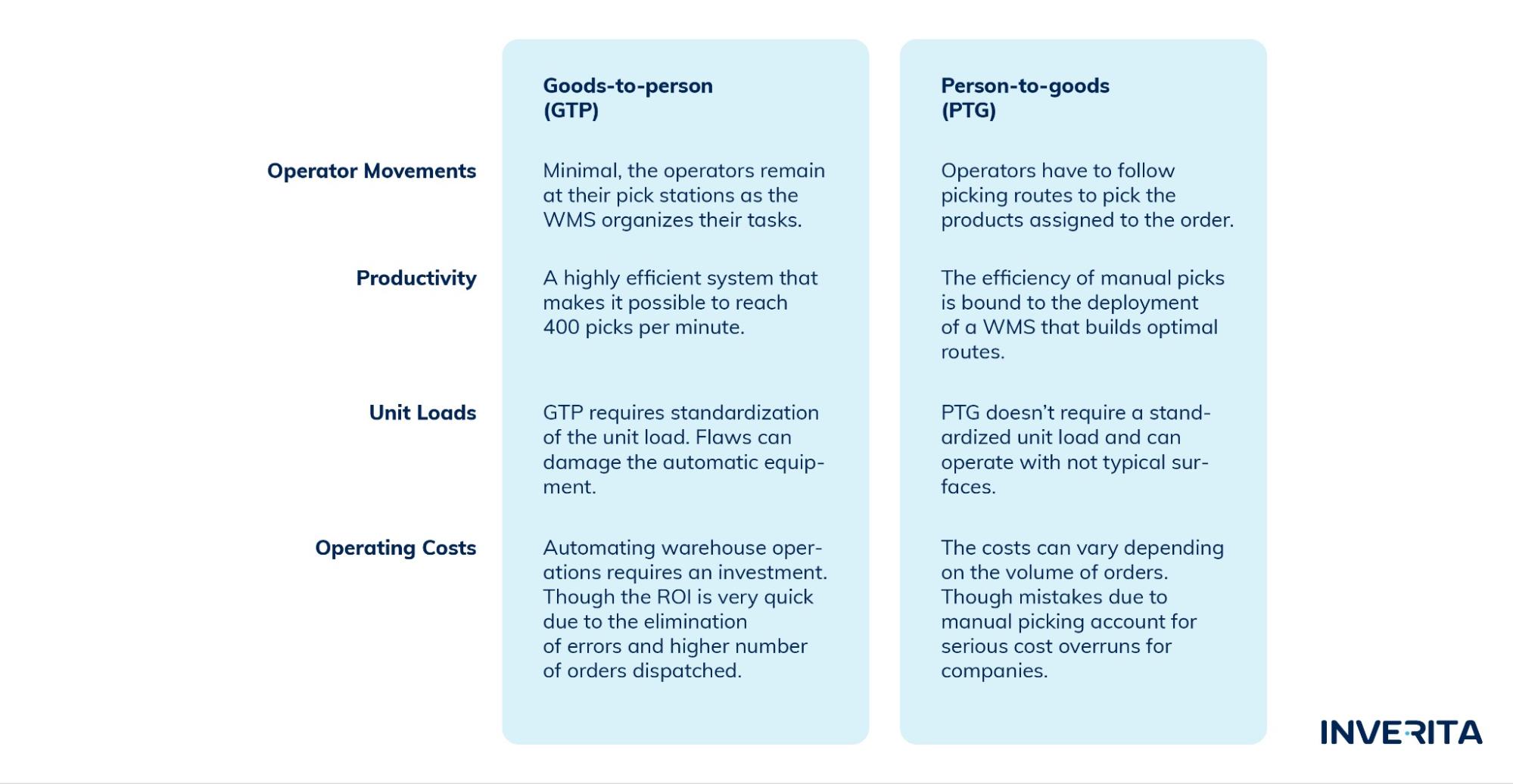
There are plenty of advantages of physical automation, including enhanced performance, increased warehouse efficiency, scalability, and employee safety.
Though these systems are best suited for big organizations with large warehouses as they require high upfront and maintenance costs and specific equipment. Some of them are:
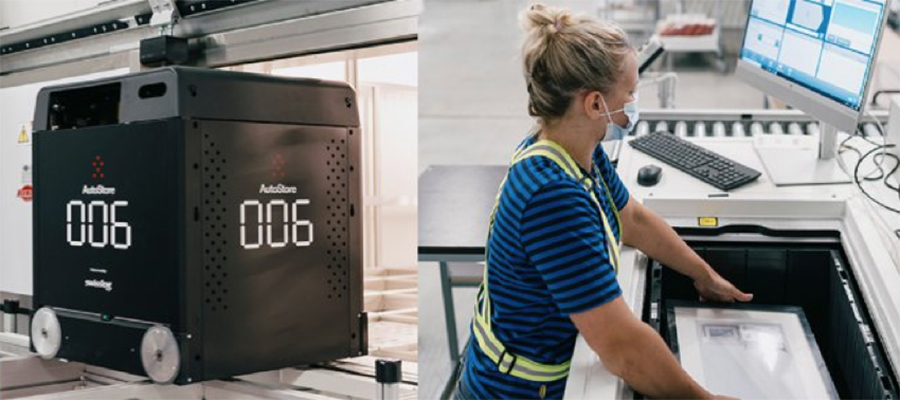
AS/RS Equipment
An automated storage and retrieval system is a complex of computer-controlled systems that automatically place and retrieve loads from required storage locations. The technology includes cranes, shuttles, vertical lift modules, and other systems that are integrated with WMS and WES.
There are many different types of such systems but all of them bring powerful benefits to warehouse operations, including the ability to reclaim unused vertical space, maximized inventory shortage density, and reduced labor costs.
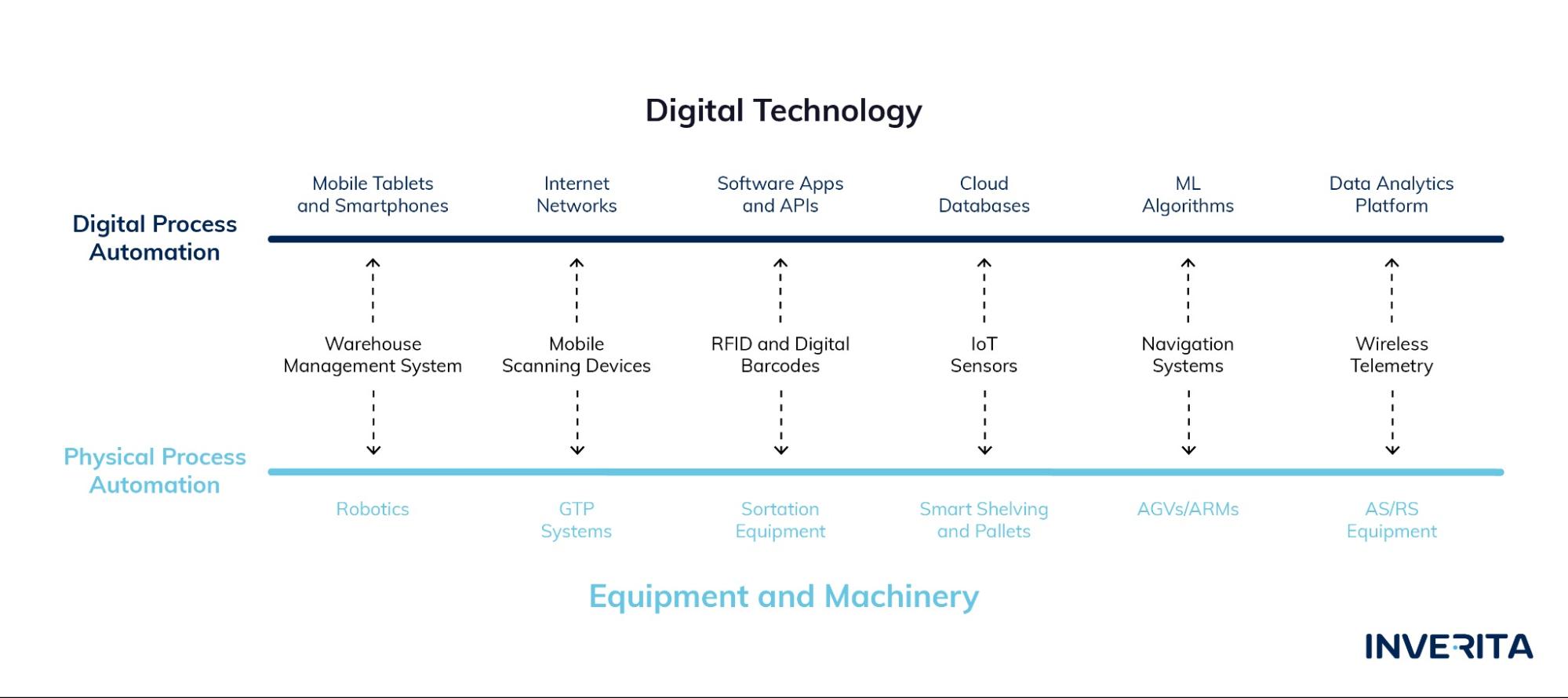
Smart Shelving and Pallets
Smart shelves and pallets leverage RFID technology to track inventory in warehouses. With the weight sensors embedded in racks or underneath, they can track the sum of inventory sitting on the shelves. This way, warehouse managers can check inventory levels in real-time and know when the product is out of stock.
AGVs/ARMs
An automated guided vehicle is a pre-programmed vehicle that is used to transport goods in the warehouse and is usually guided by wires or magnetic strips installed on or under the warehouse floor.
An autonomous mobile robot can move items without any physical guides, just by using sensors and processors. This robot can learn the locations inside the warehouse and plan its route itself.
How Does Warehouse Automation Work?
Since we’ve already discussed what is automated warehouse, let’s see how automation works.
If you need to put 10k pairs of the same trainers into boxes, doing it by hand will take hours of boring work.
If you need to keep track of which items are moving in and out of your warehouse, and where specific inventory is located, it will require a dramatic amount of human labor and time.