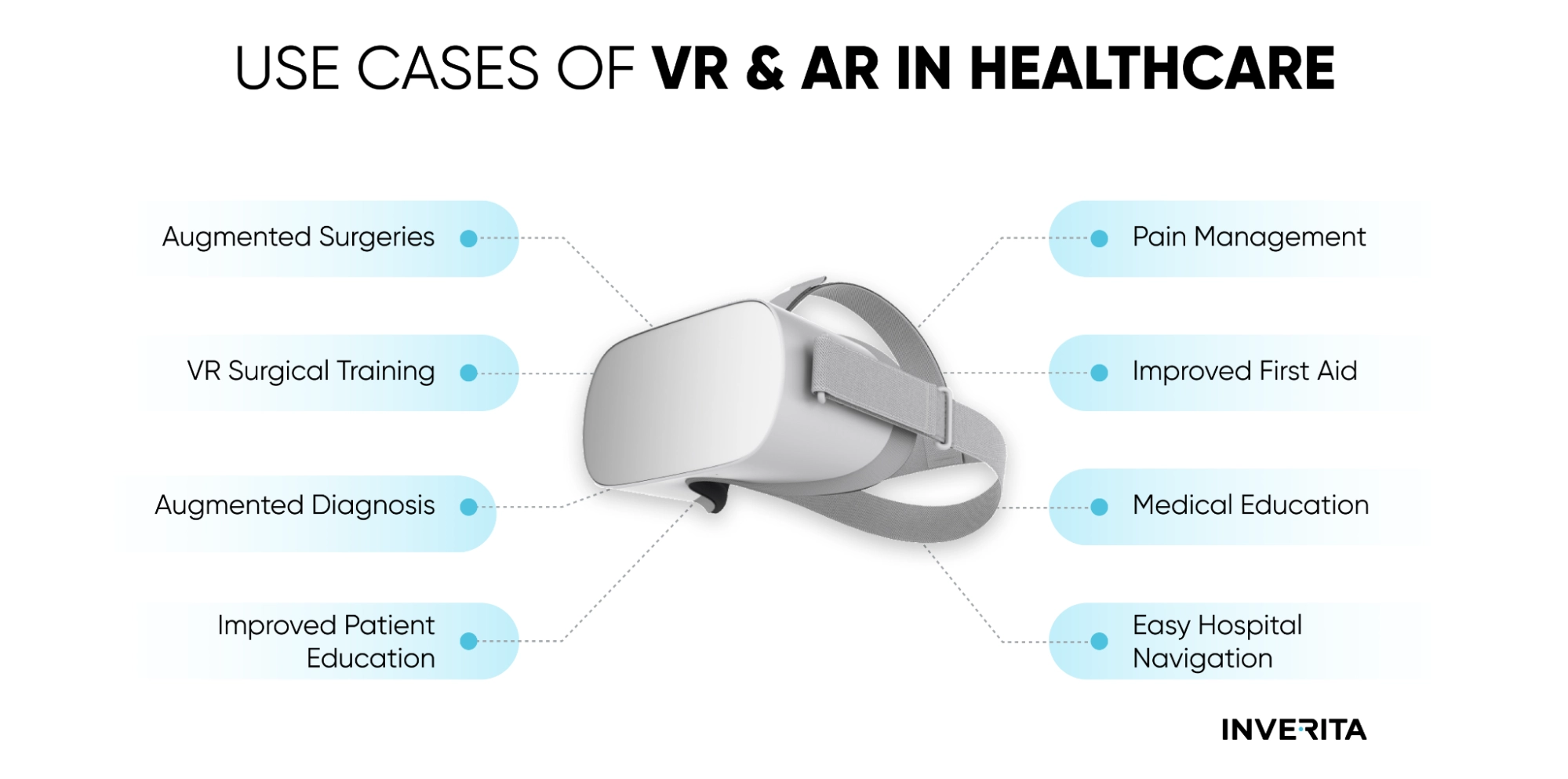
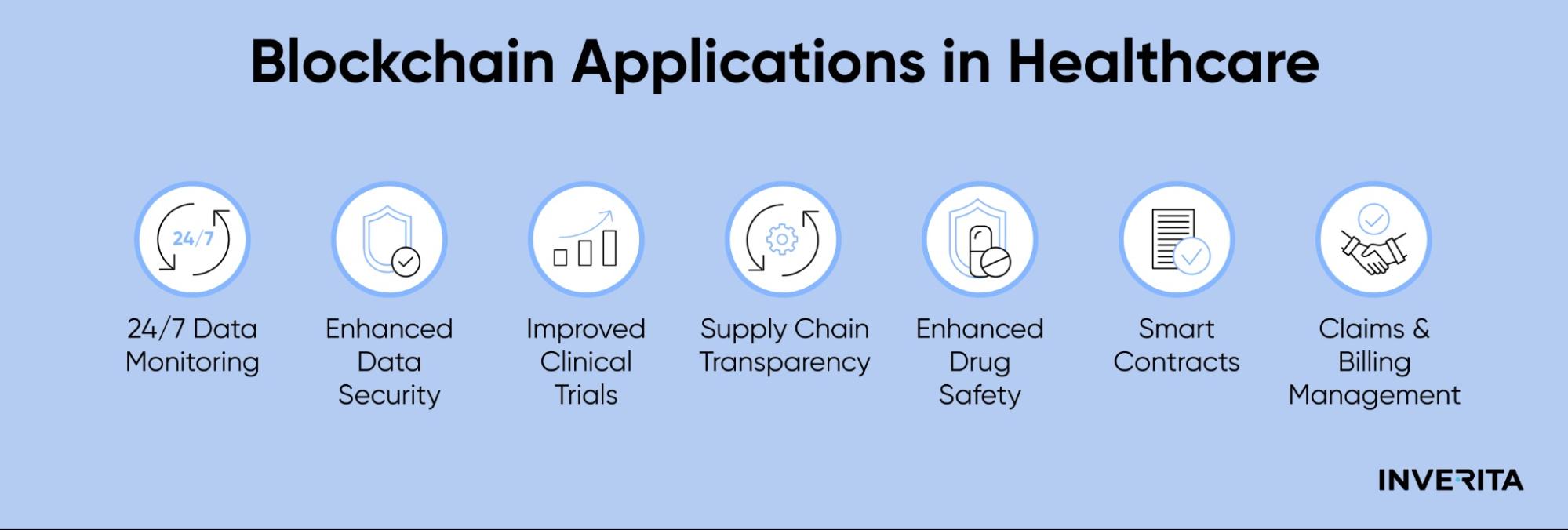
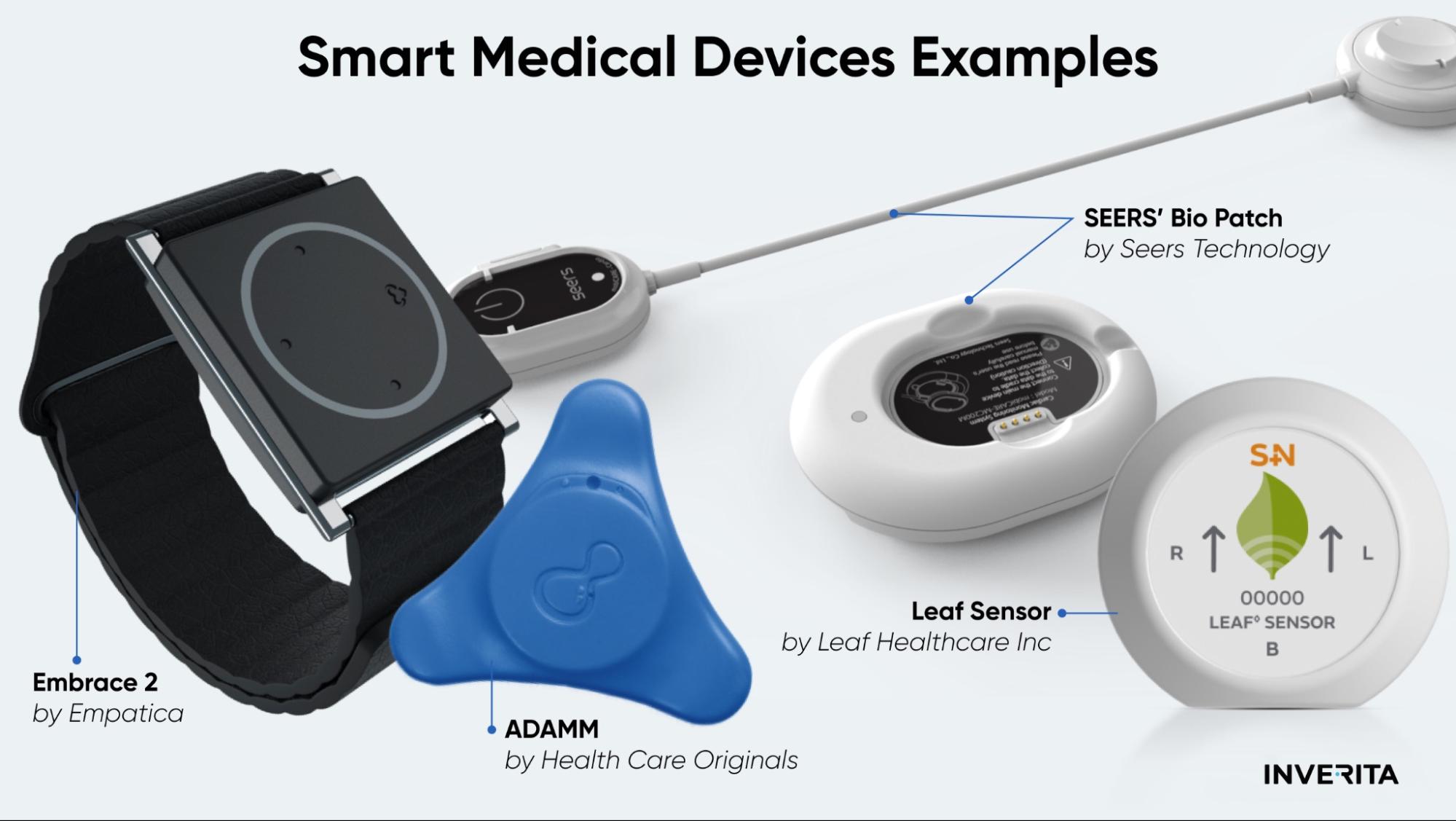
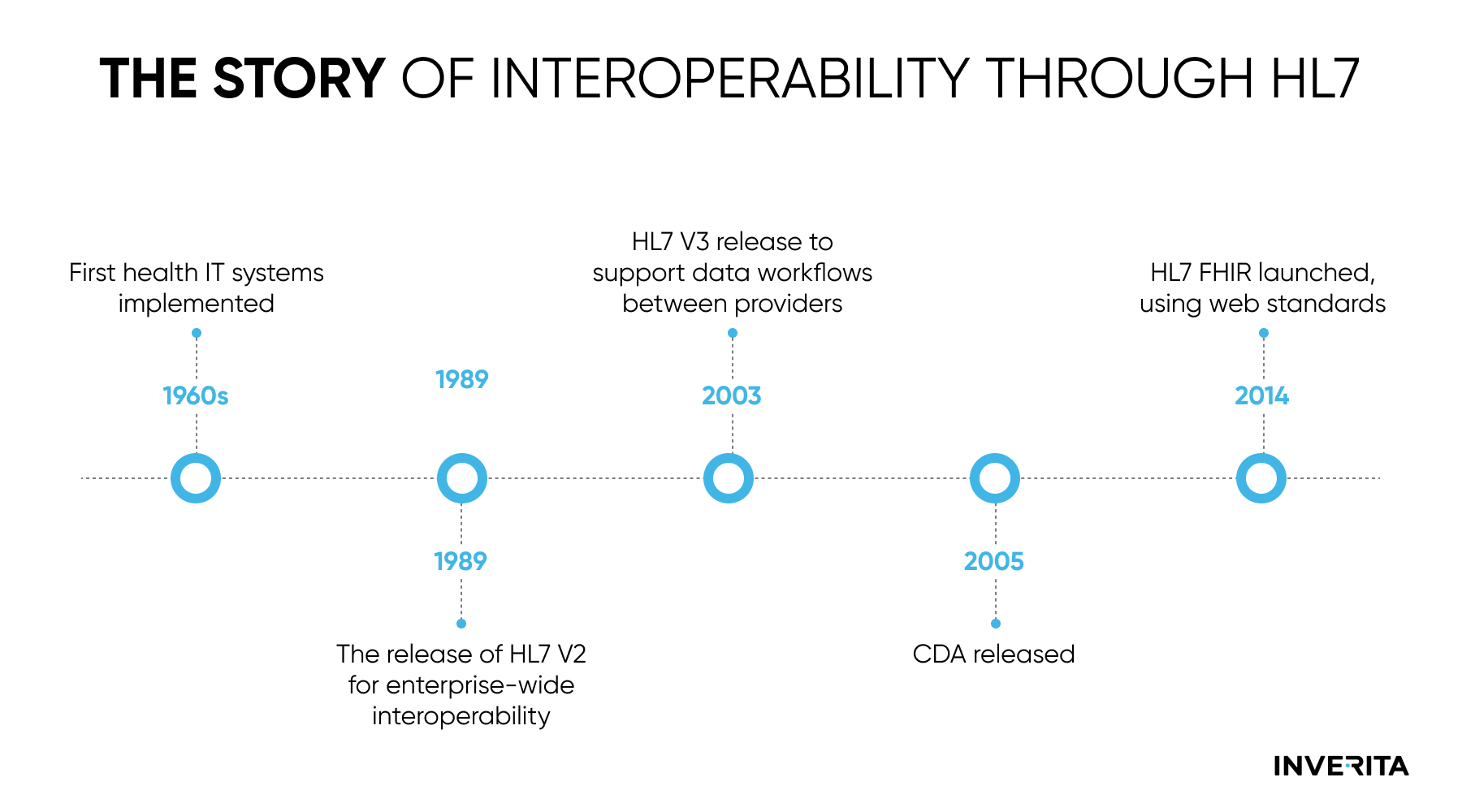
As telemedicine progresses, the physical barriers between doctors and patients become more invisible. Yet, video consultations still lack the personal touch of face-to-face visits.
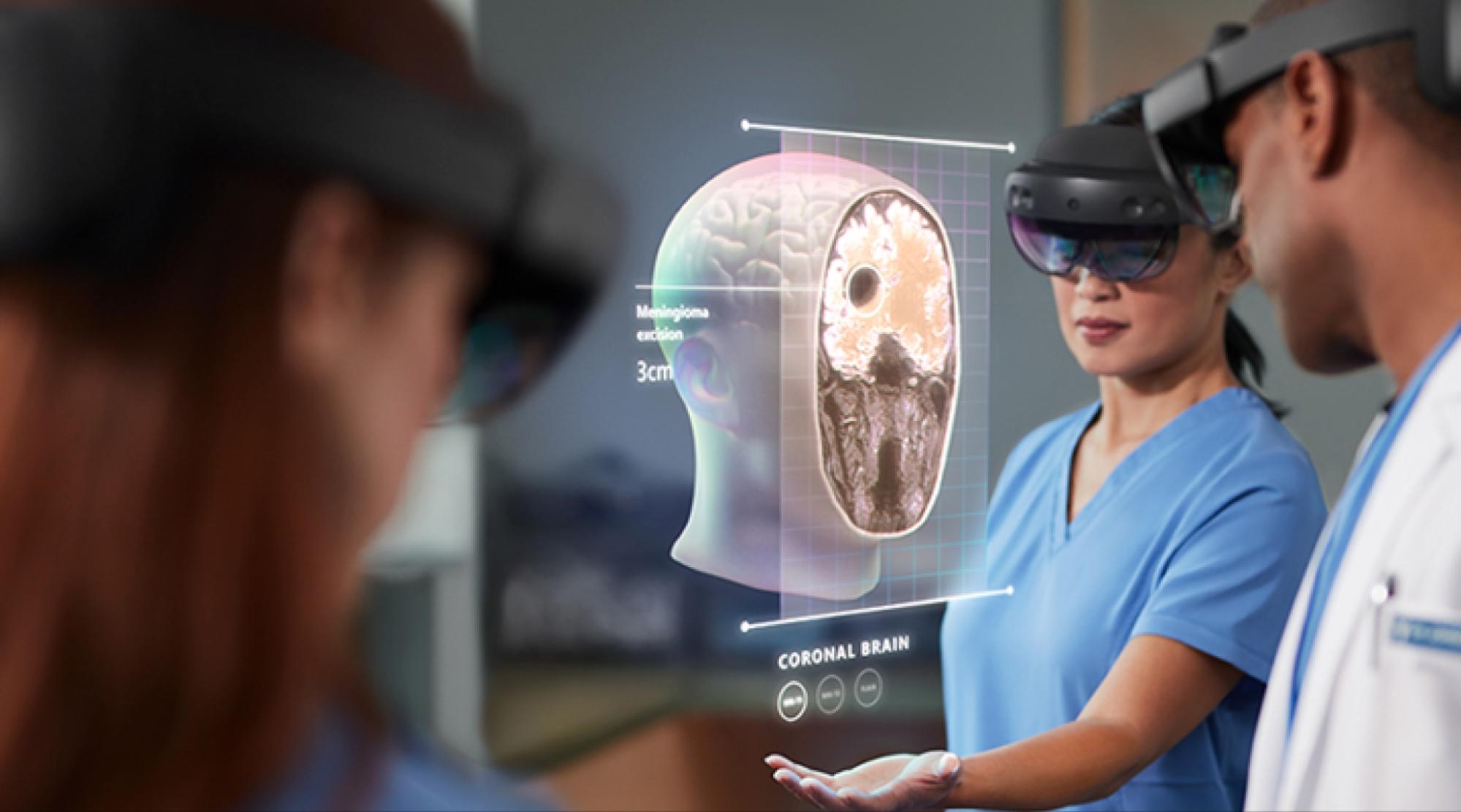
Here enters the concept of virtual hospitals. These digital facilities replicate the look of real medical settings, enabling patients and healthcare providers to engage in virtual consultations using avatars.
Additionally, this concept may incorporate telepresence technologies, allowing healthcare providers represented by avatars to virtually "visit" patients in their homes.
Patients with similar health conditions can join support groups and communities to share experiences and provide emotional support. Meanwhile, doctors can collaborate with peers, discuss cases, and master their skills using 3D models and simulations.
Of course, it isn’t a matter of a year or two when virtual hospitals become a part of our healthcare routine but it’ll likely become one of the technological trends in healthcare in the near future.
# Telepsyhiatry
Virtual mental health consultations have surged among prominent technology trends in healthcare industry, outpacing other specialties in 2026 with a notable 37% of mental health visits occurring online by the third quarter.
This shift is critical as mental health issues continue to escalate, exacerbated by a shortage of healthcare providers. In the United States alone, one in five adults reports unmet mental health needs, highlighting the pressing need for accessible care. Telemedicine serves as a vital solution, offering convenient avenues for mental health and substance use treatment.
Through regular check-ins, therapy sessions, and real-time monitoring, telemedicine helps prevent the worsening of substance-related disorders and mental health challenges. By removing traditional barriers to seeking help, virtual appointments foster a supportive environment where individuals can address concerns before they escalate.
# Artificial Intelligence
AI is poised to revolutionize drug development, offering immense potential to accelerate the traditionally slow process of discovering new medicines. Historically, it has taken up to 26 months to initiate clinical trials, but AI can drastically reduce this timeframe by forecasting optimal drug candidates and crafting customized medications tailored to specific targets. Notably, the first drug entirely designed through AI has entered clinical trials in China, with projections suggesting that AI could introduce 50 new therapies within the next decade, potentially saving billions in development costs annually.
Additionally, AI is making notable strides in healthcare diagnostics and treatment, as evidenced by the FDA's approval of numerous AI-enabled medical devices. These range from smartwatch sensors capable of detecting atrial fibrillation to advanced algorithms for disease detection through image reconstruction. These innovative tools promise to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility in healthcare.
Furthermore, medical facilities are developing direct-to-patient solutions for triaging and offering advice through voice or chat-based interactions, ensuring swift and scalable access to address basic questions and medical concerns. This approach has the potential to reduce unnecessary visits to general practitioners, easing the burden on primary healthcare providers. Moreover, it can provide essential guidance to populations in remote or underserved areas, where access to medical expertise may be limited.