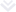
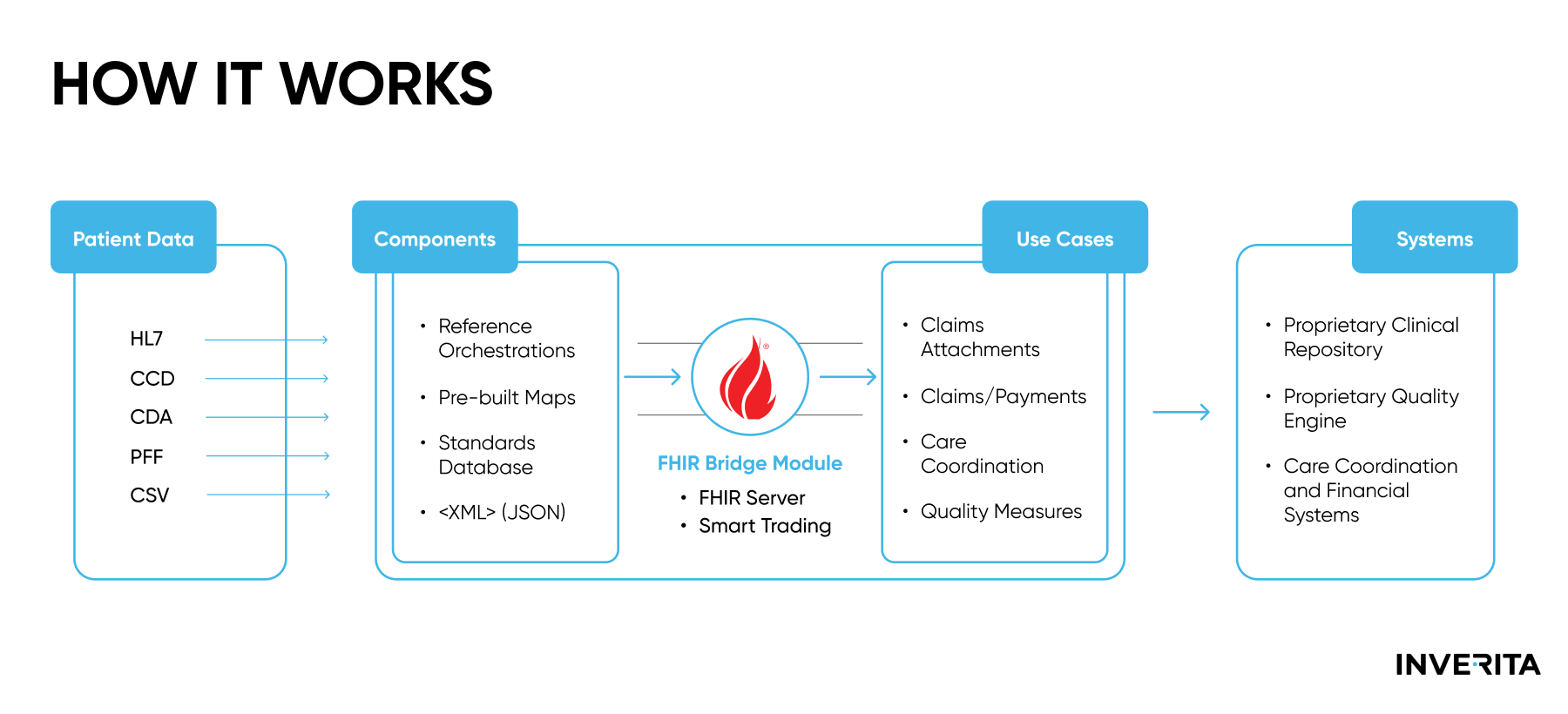
HL7 version 2 was introduced for the first time in the late 80s and is a non-XML encoded syntax with segments and delimiters. In order to identify segments a 3-character identifier is used. Each segment consists of a standard set of fields (composites) which are separated by the delimiter and can have sub-fields, or sub-composites with sub-delimiters, respectively. Each segment is divided by carriage return from the others and fields are separated by a ‘|’ delimiter, and, finally, ‘^’ separates sub-components.
Every message starts with the ‘MSH’ segment, which identifies key message data like sending and receiving systems, message type, version, or timestamp. HL7 v2 has multiple release versions from 2.1 to 2.8 offering backward compatibility across them.
HL7 version 2 messaging is fully supported by all Electronic Medical Records systems in the United States. The general acceptance and support of this standard made it a suitable protocol to connect various systems, especially within one organization. Those interfaces are still in use and when someone refers to “HL7”, most likely this person has HL7 v2 in mind.
Despite being so popular, HL7 v2 also has its downsides. The syntax used by HL7 v2 is quite challenging in application development. Every single message contains many data elements that might be not relevant to some workflows. Additionally, since the standard is event-driven, the frequency of message generation is high, which means that some unwanted traffic might be created on a particular interface. Also, HL7 uses Minimum Lower Layer Protocol, which relies on IPsec or Transport layer Security while communicating outside a secure network. Considering this, one can assume that the HL7 v2 protocol works well when connecting applications within the same hospital or healthcare system since those are usually on the same network, however, it becomes bulkier when linking applications and systems on multiple networks.
HL7 messaging version 3 was introduced in the 1990s as a standard that is intended to support all healthcare workflows. The previous version provided a standard for implementation; however, it was still quite difficult to support at scale across many systems due to the significant localization that occurs in messages. HL7 v3 tries to ensure a more rigid message structure compared to the previous standard while supporting interactions like events in HL7 v2. HL7 v3 messages rely on XML encoding syntax and follow object-oriented principles.
The intention of HL7 version 3 was good, but due to its complexity healthcare software community found it challenging to implement. Additionally, no backward compatibility with version 2 was offered, hence organizations willing to use the new standard were forced to completely migrate to the new one. As mentioned earlier, when someone refers to HL7, in the vast majority of cases they think about v2, not v3, and bad perception of the third version is one of the reasons for that.
FHIR Explained
What is FHIR?
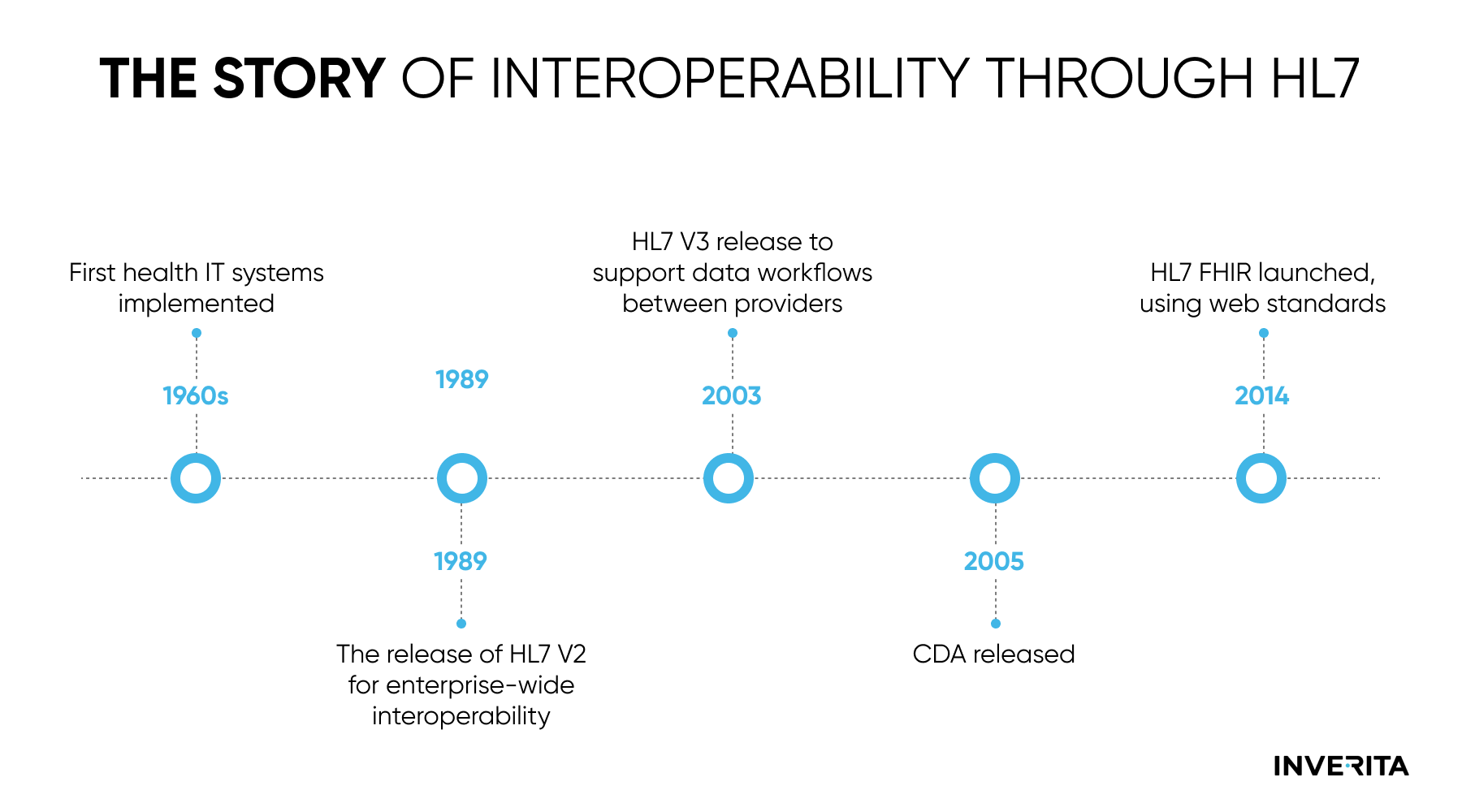
The Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR, pronounced “fire”) standard is a set of rules and specifications for electronic healthcare data exchange. It became a next-generation standards framework that combines the best elements of HL7 v2, HL7 v3, and HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) leveraging the most modern web service technology at the same time. FHIR design is based on RESTful web services and consists of modular components, or ‘resources’, and supports both JSON and XML. Specific resources can be accessed through a discrete URL, which allows for their retrieving, sending, and manipulation via an API request.
Sometimes FHIR resources are similar to HL7 segments of the messaging version 2, however, there are no standardized conversion rules or direct relationship between the two. Conversion of healthcare data between various HL7 standards is relatively tricky, and the FHIR structure is completely different from the structure of other message types.
Exploring the FHIR Standard
FHIR is deemed to be a standard that is easier to learn and implement, especially for developers who started their careers in recent years and specialize mostly in web services. It uses more efficient data structures that are flexible and extensible. It has greater scalability potential, better cost efficiency, and is directed towards future healthcare interoperability.
HL7 International released FHIR Normative version 4 in 2019, and this standard is built to be backward compatible with all next versions of FHIR. There is a global tendency to build new cloud-based healthcare and other digital health-related applications that employ architectures that support web-service protocols like FHIR.
US regulatory bodies like the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (ONC) have already published new rules that require the usage of API to enable access to patient information, and that’s where FHIR can demonstrate its strength.