Step-by-Step Process of Healthcare EDI
Explore the step-by-step breakdown of how EDI facilitates the exchange of healthcare information.
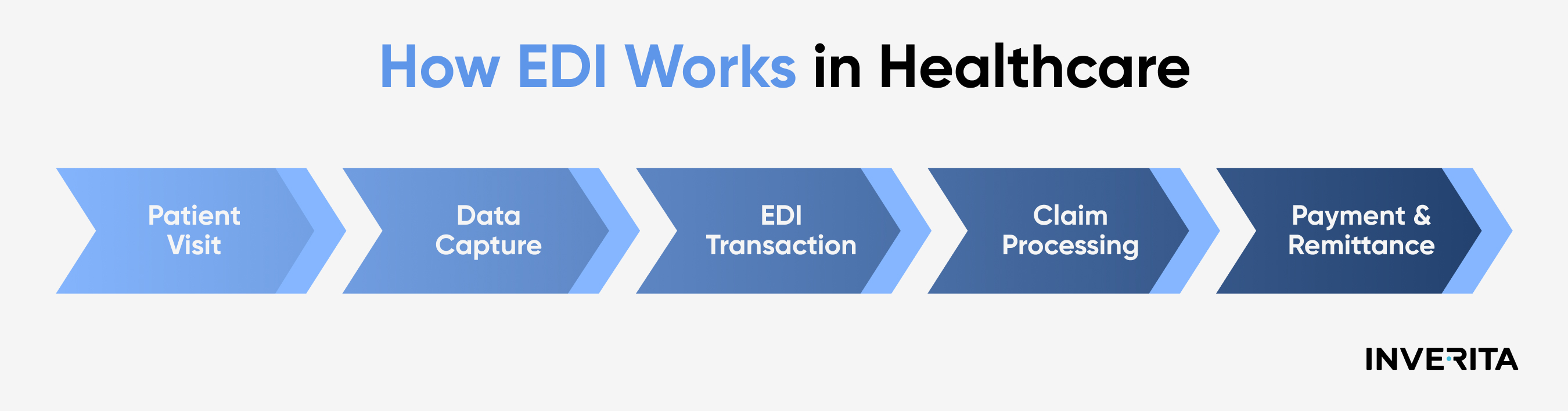
Data Preparation and Transmission
Healthcare professionals collect patient information, insurance details, and treatment codes from diverse sources and format this data following standardized EDI formats like ANSI X12 to ensure consistency and compatibility across systems. Before transmission, this information is encrypted to comply with security and privacy regulations.
Data Validation and Forwarding
The formatted data is sent to a clearinghouse, which reformats it, checks for formatting errors, verifies patient identifiers and procedure codes against relevant databases, and ensures compliance with EDI standards and regulatory requirements. If discrepancies are found, the data is returned to the provider for correction. Once validated, the data is forwarded to healthcare payers.
Payer Processing and Response
The payer, such as an insurance company, processes the submitted data, reviews claims, verifies coverage, and determines reimbursement amounts. After that, required updates to patient records are made, followed by the payment processing and scheduling.
EDI Acknowledgments and Responses
After processing, the payer sends an acknowledgment confirming data receipt and claim status back to the clearinghouse. Providers receive detailed responses, including payment details or necessary adjustments, allowing them to update medical records and resolve any issues efficiently.
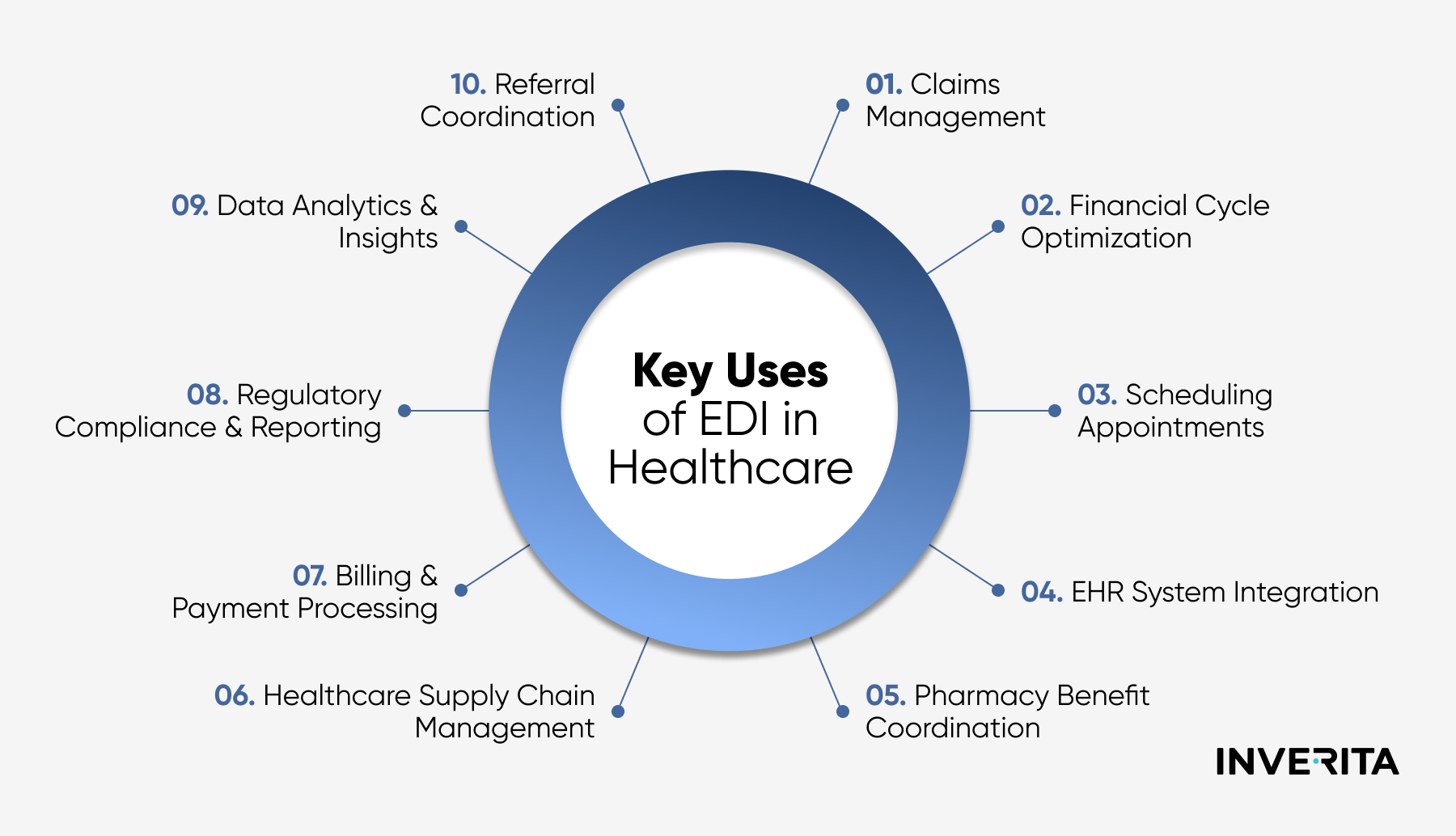
EDI Use Cases in Healthcare
Electronic data interchange spans a variety of aspects within clinical operations and patient care. From claims processing to regulatory reporting, EDI fuels productivity, accuracy, and compliance across multiple healthcare functions.
The most common applications include:
- Claims processing. EDI automates the submission and processing of claims while ensuring correct formatting and checking for all the necessary details. This minimizes paperwork, reduces errors and rejections, and accelerates healthcare processes.
- Appointment scheduling. EDI streamlines scheduling by enabling real-time data exchange between healthcare providers, patients, and referring physicians. This ensures accurate scheduling, reduces double bookings, and enhances patient care coordination through timely notifications and reminders.
- Laboratory orders & results. By integrating EDI into laboratory workflows, providers can electronically transmit orders and receive results in real time. This also ensures that lab results are instantly available within patients' EHRs, minimizing risks related to manual data entry.
- Healthcare analytics. With EDI systems, healthcare organizations can analyze standardized data for population health management, performance measurement, and strategic decision-making, track trends, optimize resource allocation, and continuously improve patient care.
- Pharmacy benefits management. Pharmacies and healthcare providers integrate EDI to verify patient eligibility, process prescription claims, check drug formularies, and optimize payments. This facilitates the entire prescription management process and minimizes medication errors and delays.
- Regulatory compliance reporting. EDI ensures healthcare organizations meet compliance requirements by automating the accurate and timely submission of HIPAA transactions, quality reporting, and public health data.
- Patient billing & statements. EDI streamlines invoice generation, electronic payment processing, and statement delivery while maintaining accuracy and improves providing patients with clear, timely billing information.
- Supply chain management. EDI optimizes healthcare supply chains, ensuring timely delivery of medical supplies, minimizing shortages, and improving cost efficiency through accurate and consistent inventory tracking.
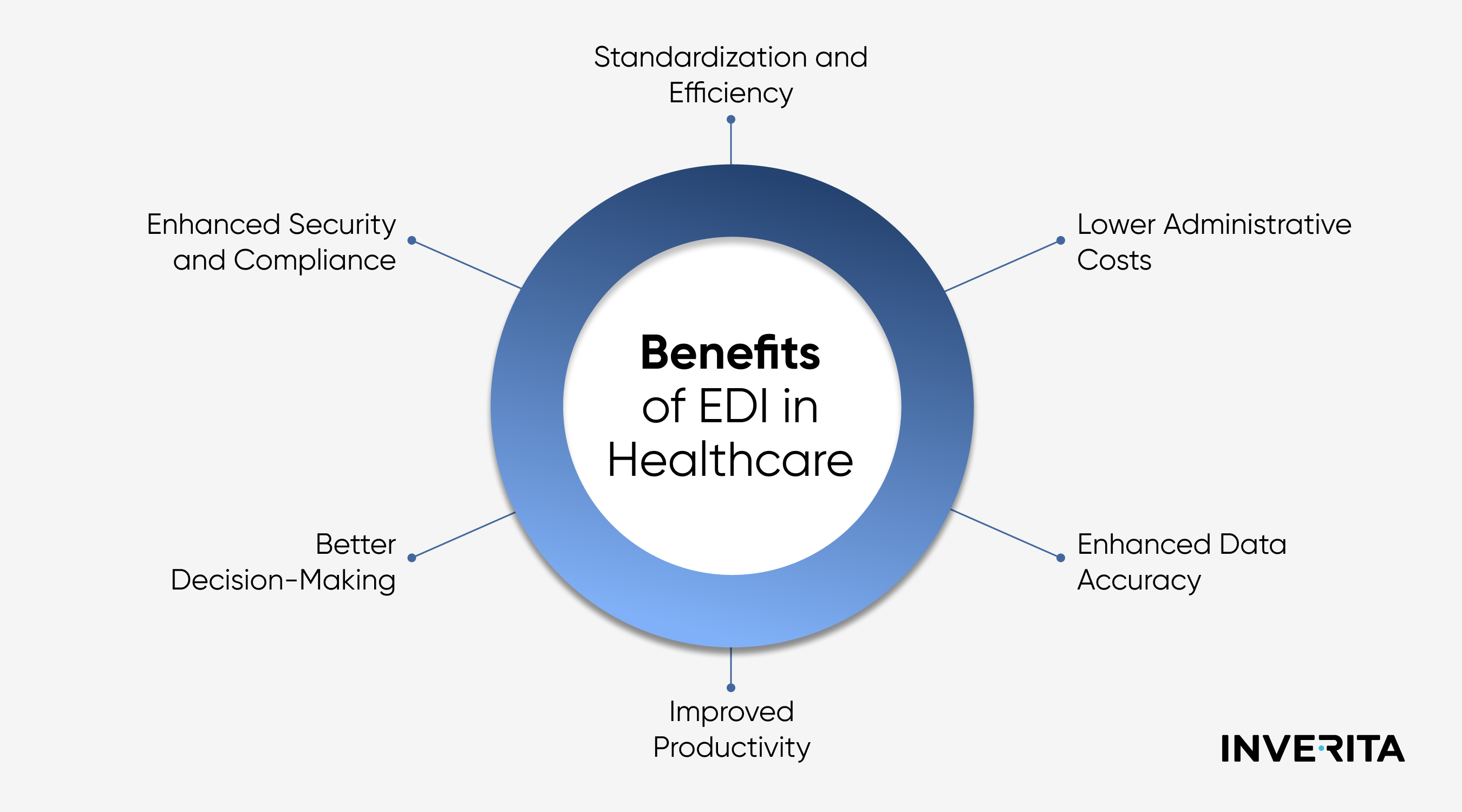
The Importance of EDI in Improving Patient Care
The modern healthcare system faces the pressing demand for more efficient, patient-oriented, and value-based services. EDI systems bring a new level of automation that increases productivity, enhances collaboration between providers, and allows for quick and smooth data sharing, better care coordination, and informed decision-making. The undeniable importance of medical EDI lies in its impact on accuracy, resource optimization, and regulatory compliance.
- Streamlining Healthcare Operations
- Minimizing Errors and Delays
- Facilitating Faster Claim Processing and Reimbursement
- Supporting Better Clinical Decisions and Patient Outcomes
Implementing EDI in Healthcare Systems
Implementing an EDI system in healthcare requires careful planning, selecting the right technology, and ongoing optimization. These key steps will guide you through this process:
- Needs assessment. Evaluate your current workflows, data exchange requirements, and regulatory compliance needs to find the software solution that matches your operational objectives.
- Choosing system. Select an EDI solution that integrates seamlessly with your existing IT infrastructure and supports essential transactions. Prioritize scalability, ease of use, and vendor support.
- Training and adoption. Train your staff to use the EDI system effectively, focusing on data entry, reporting, and analysis. Inform them about transaction sets, procedures, and policies.
- Monitoring & improvement. Regularly assess the system’s performance, collect user feedback, and collaborate with the healthcare EDI provider to maintain efficiency and reliability.
EDI and Healthcare Compliance
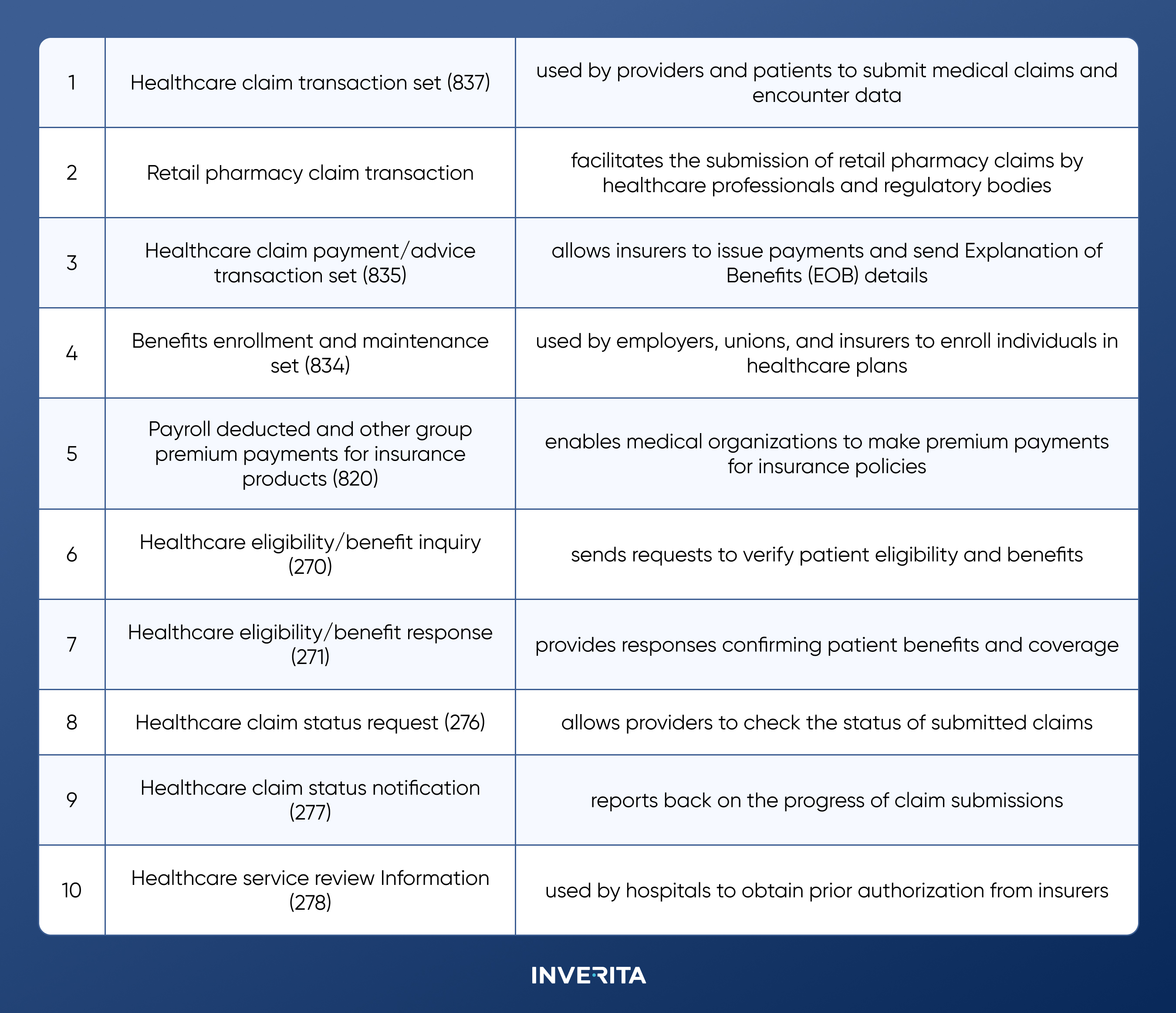
EDI compliance in healthcare ensures secure, standardized, and legally compliant data exchange. It aligns with key regulations like HIPAA, which require secure electronic transactions and data protection. Compliance is reinforced through audit trails, encryption, and consistent claims processing. Common EDI standards in healthcare include ANSI X12 (used in the US) and EDIFACT (global standard).
How EDI Will Evolve and Improve the Healthcare Industry
EDI reinforces the shift towards streamlined and standardized communication within healthcare so its role across the industry will keep expanding, driving greater efficiency, accuracy, and interoperability.
As technology evolves and healthcare institutions adopt it increasingly, EDI seems to be one of the major game-changers in the near future, bringing a higher level of innovation to clinical workflows.
With deep expertise and long-term experience in healthcare software development, inVerita delivers cutting-edge medical solutions that address industry challenges and improve care delivery.
Let’s work together to build smarter, tailored healthcare systems. Contact us now for more details!