The Breach reports to the Office for Civil Rights recorded 225 hacking-related incidents just in half a year that affected more than 21 million people.

Compliance with Healthcare Industry Standards

Technology Expertise and Continuous Innovation

Given the healthcare data security challenges, providers must make a genuine effort to ensure the security of their patient’s information and steer clear of the misfortune of hundreds of healthcare providers that lost millions of dollars and most importantly - their patients’ trust. This blog aims at giving you an overview of the most common healthcare cybersecurity threats and tips on how to overcome them.
Phishing prevails in data security issues in healthcare. With one wrong click, such attacks can dismantle the entire healthcare system, stealing patients’ personal data and encrypting files. Phishing scams have claimed hundreds of thousands of patient financial data, healthcare records, and other sensitive personally identifiable data.
There are various types of phishing: email, spear, whaling, smishing and vishing, and pop-up phishing. Below, they are briefly explained.

The largest and the most expensive data breach in healthcare so far happened in Anthem Inc in 2014. The health information of 78.8 million people was stolen due to an employee opening a phishing email. The company was fined $16 million and a multi-state action was settled with a state attorney for $48.3 million, adding a class action lawsuit with breach victims for $115 million.
Healthcare organizations are highly dependent on access to patient records which makes them a very frequent target for this type of healthcare data security issues. According to a report from the cybersecurity company Sophos, 67% of healthcare organizations were hit by ransomware attacks last year which is a 7% increase from 2023
Ransomware is a type of malware that infects systems and makes them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Usually, ransomware infects systems and files in one of the following ways:
This type of cyber security risks in healthcare has significantly evolved over the last few years, applying new tactics, techniques, and procedures to make it difficult for security systems to keep up with. There are even platforms such as ransomware as a service, using which, anyone even with no technical knowledge can launch a ransomware attack.
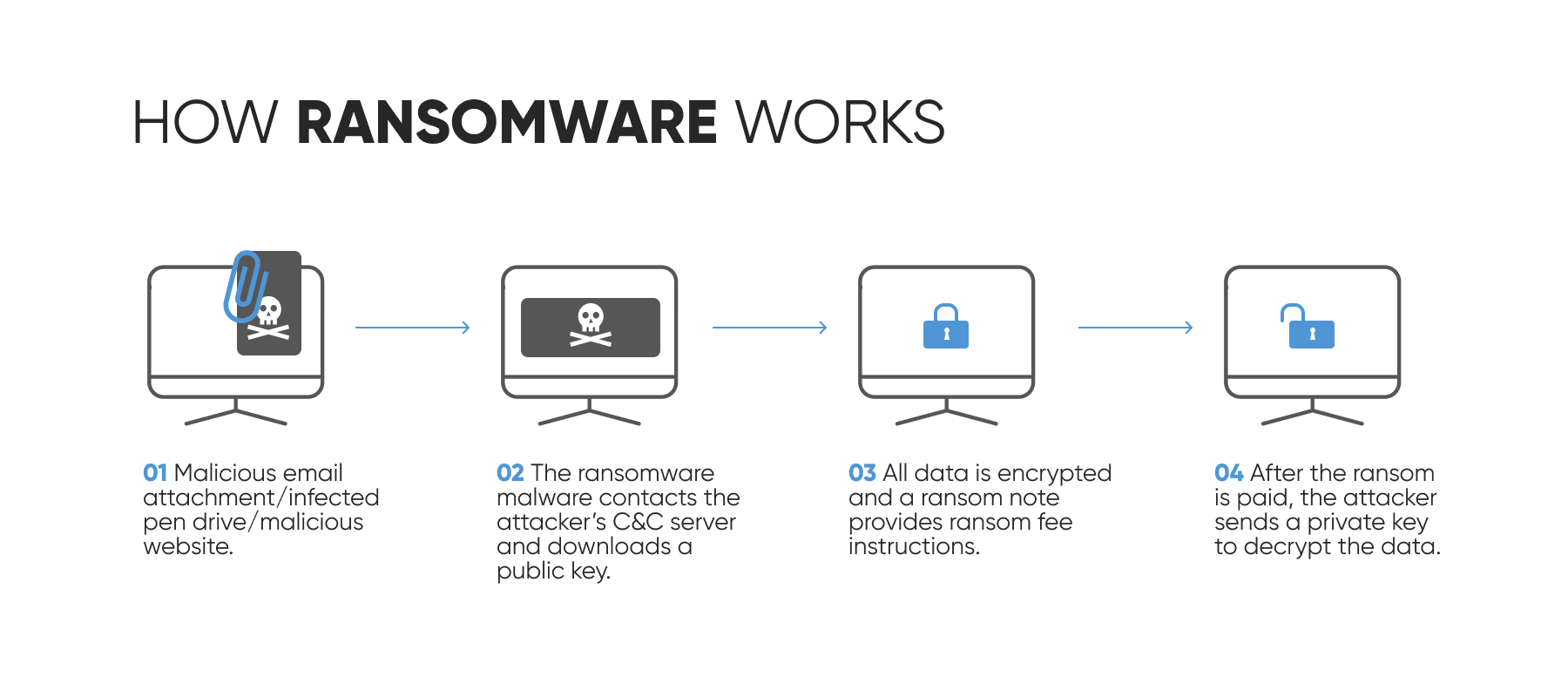
Paying the ransom, however, is not the only cost healthcare organizations end up paying for a ransom attack. Most of the providers lose their business or revenue due to the inability to operate.
Breaches are widely spread among cybersecurity challenges in healthcare and can be caused by various types of incidents, including credential-stealing malware. According to IBM Security's annual Cost of Data Breach Report, a data breach in healthcare now has a record-high price tag, approximately $10.1 million on average.
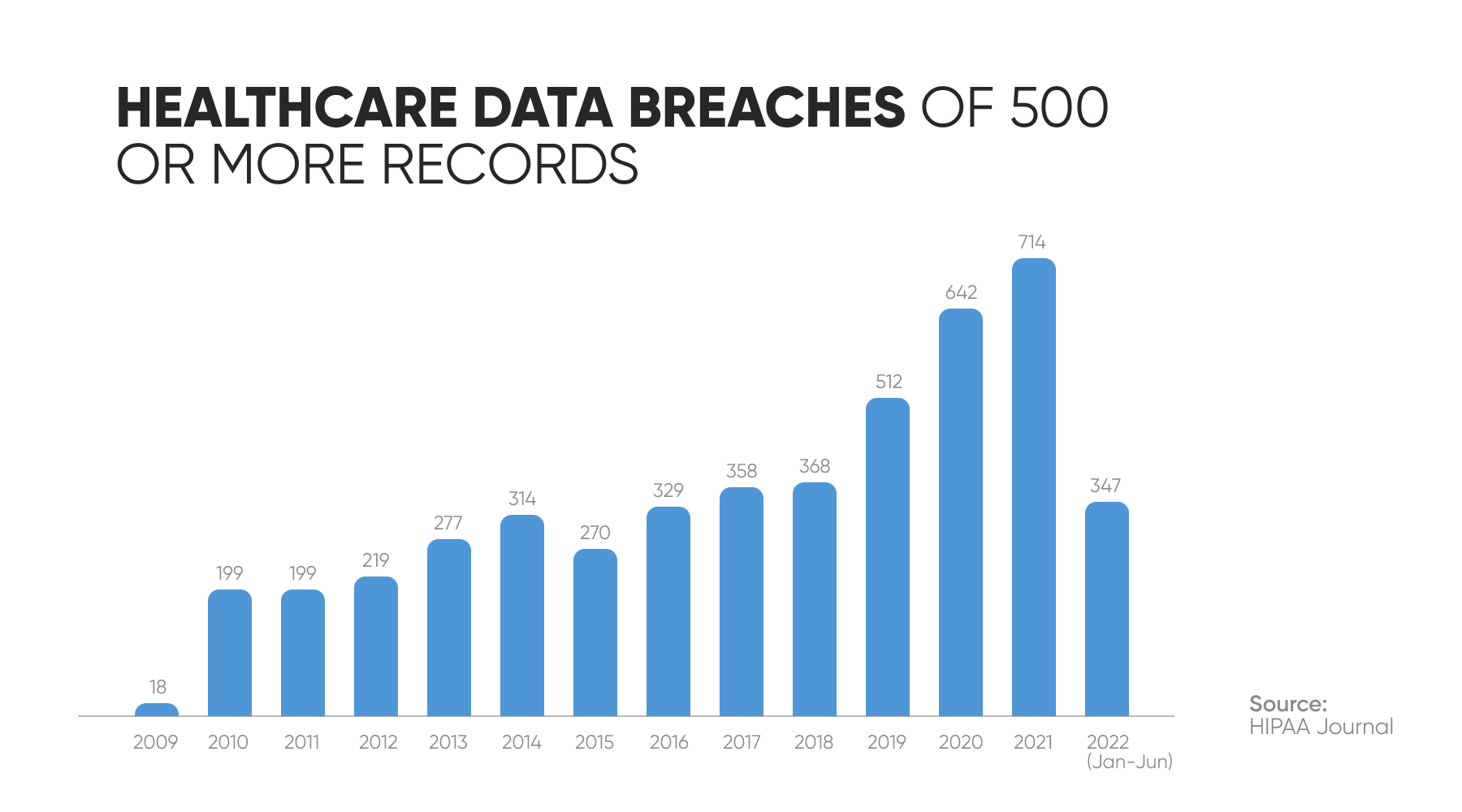
During the last few years, the number of healthcare data breaches has significantly increased. For example, the number of total victims jumped from 14 million in 2018 to almost 40 million in 2023.
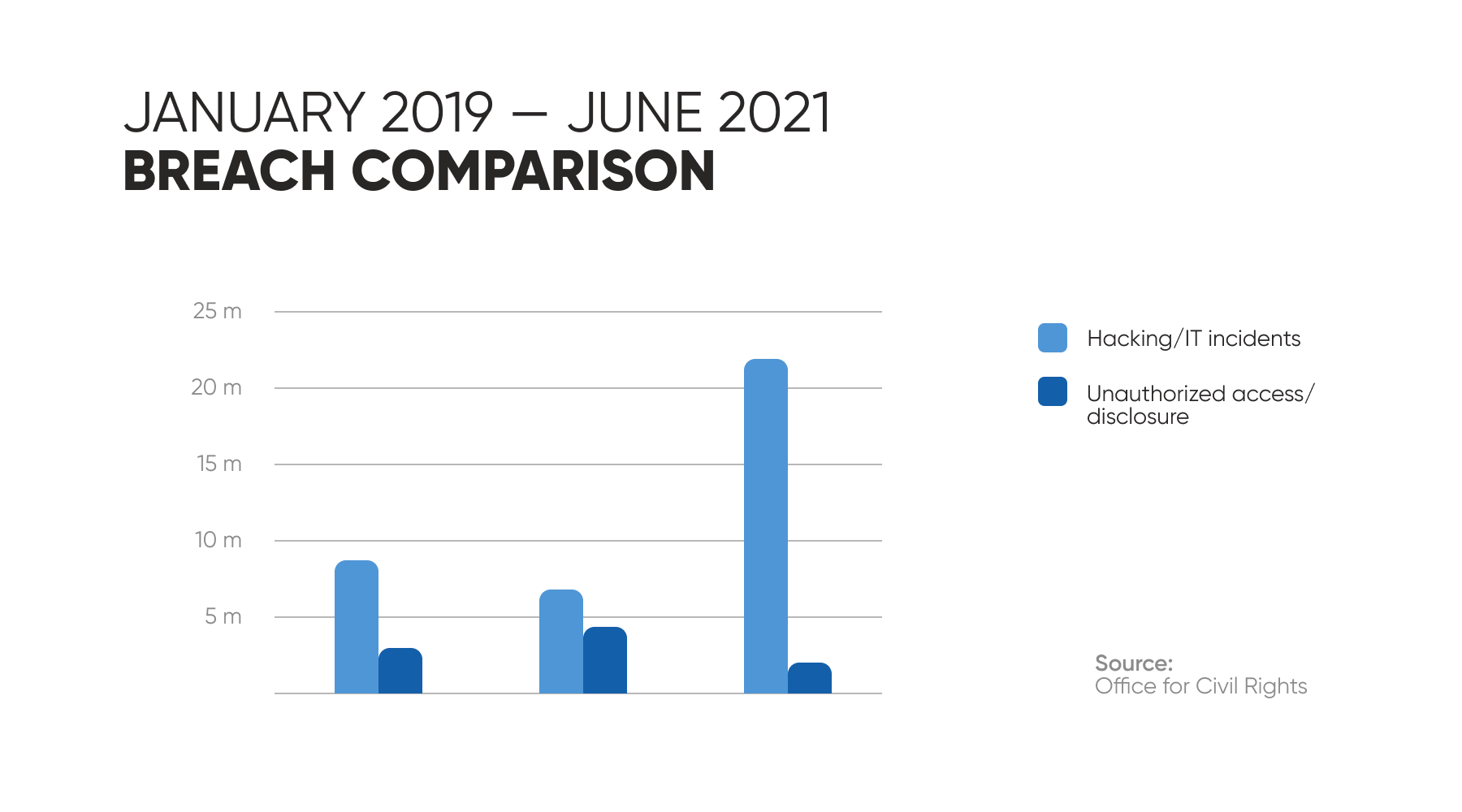
The top reasons for data breaches differ from those of other industries and are mostly caused by internal actors rather than external ones. For instance, human error and privilege misuse were reasons for more cyber security problems in healthcare organizations than hacking and malware.
Here are the top 5 causes of data breaches in healthcare:
Around one-third of all data breaches are caused by misdelivery, disposal error, publishing error, misconfiguration, and loss of documents.
Almost another one-third of cybersecurity challenges in healthcare are caused by a person abusing their use of internal resources.
Most of the physical causes occur due to theft of the records stored on computers or paper documents.
Gaining unauthorized access to a system or device.
Malicious software, in particular, ransomware.
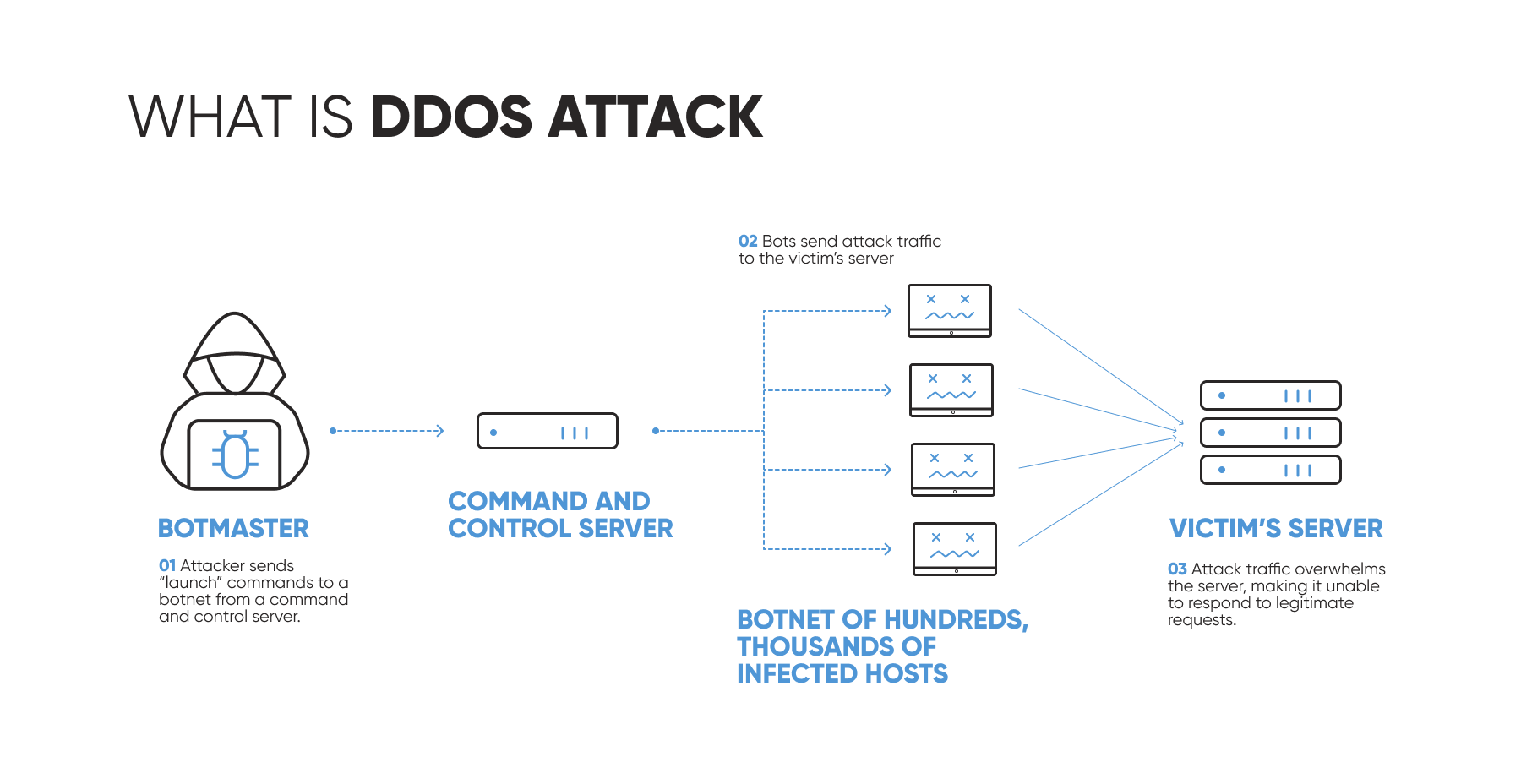
Distributed denial of service, or shortly DDoS attacks is another widespread type of healthcare cybersecurity issues that poses a serious problem for service providers. They can completely halt business operations and restrict access to vital IT resources. Cybercriminals often launch DDoS attacks to distract the attention of security teams while performing more malicious activities, for example, infecting systems with ransomware or extracting data. In the worst-case scenario, the healthcare systems can be compromised leading to a loss of patient data.
Cybersecurity challenges in using IoT in healthcare are also among the starting points for major security issues. Therefore organizations must keep all their IoT devices up-to-date and move those devices they don’t control directly into an isolated network.
Healthcare legacy systems create a special type of cyber security challenges in healthcare. These are the systems that are no longer supported by their manufacturers. This may refer to both hardware and software. For example, in the case of hardware, if you have outdated physical servers you wouldn’t be able to fix them and in the case of software, it would be impossible to make any performance or security improvements. Legacy systems also include different devices, apps, operating systems, and even processes. In terms of security, it means that in case of any security issues in legacy systems, healthcare providers should compensate for all the costs themselves.
The first step toward protecting an organization from one of the most common cyber security issues in healthcare is understanding the attacker’s tactics and motives. The leadership of any organization should identify the basic indicators of phishing and explain them to their employees.
Traditional email phishing attacks usually have poor grammar and sentence structure, and include generic greetings, and a suspicious email sender address. The actors also often try to imitate a legitimate business by using an email address that resembles emails of co-workers or a boss but omits a few characters. Recipients should also pay specific attention to unsolicited emails that offer to download attachments or click a suspicious link.
There are a few important steps that every organization should take to safeguard their systems from healthcare cybersecurity challenges, especially helpful in preparing for ransomware attacks. Keep the current anti-virus version, ensure proper email filtering, and keep up-to-date backups, including storing them offline.
Also, one of the simplest security controls to implement is enabling multi-factor authentication which is able to prevent up to 90% of cyber attacks in applications.
According to the HIPAA Privacy Rule, all covered entities are to run the awareness training program for all of their employees. Unfortunately, the research shows that the healthcare industry lags behind other industries in terms of cybersecurity training despite being the main target for attackers. Only 22% of healthcare workers reported that they feel confident about their cybersecurity hygiene.
To maintain the security of their systems, organizations are required to provide their employees with training and resources on cybersecurity at least twice a year. For example, a widespread practice is sending fake phishing emails to employees to determine their level of awareness.
Additionally, patient information shouldn’t be available to all the employees in the organization so make sure you restrict physical and network access to sensitive health data.



Healthcare providers should support the relevance of their cybersecurity programs within the current cybersecurity ecosystem. Proper network and application security, encryption, and employee training should be among the top priorities of organizations to combat healthcare security challenges. Of course, none of the safeguards are foolproof but they can significantly mitigate the risk and probability of successful attacks.