Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
By implementing VR & AR technologies, many healthcare companies have managed to establish connections with their patients in terms of the pandemic, providing remote and personalized care. Passed have the times when the technologies were exclusively devoted to the gaming industry. In 2021 and beyond, VR & AR will be actively used for medical training, physical therapy, post-traumatic stress treatment, and some other purposes:
- Medical Immersion for a variety of patient needs
Healthcare providers actively leverage VR & AR technologies to enhance their patients’ experiences by engaging them in healthcare activities. A good example is the implementation of VR apps for planning the sequence of procedures and viewing the results in aesthetic medicine and orthodontia. These solutions can be also used for improved self-diagnostics and self-guided treatment in remote areas where people mainly use telemedicine. Another implementation of AR is mapping assisting which users can define the nearest clinics in unknown areas, which is especially useful in case of emergency.
Surgeons can use VR & AR solutions before performing an operation to walk through the organs or view 3D models of challenging surgical cases. What is more, such 3D organ models can serve illustrative purposes in the learning process or explain to patients the whole surgery process. According to a Harvard Business Review study, surgeons that trained with VR solutions had a 230% boost in their performance in comparison to their traditionally trained colleagues.
Such software programs provided by Osso VR and Immersive Touch are already in active use and give promising results.
The technology has also been proven to be effective in reducing pain. The research shows that patients who suffered from post-surgical, cardiac, or gastrointestinal pain, have shown a decline in pain levels while using VR to distract them from painful stimuli. Also, women in labor who were equipped with VR headsets to visualize soothing landscapes managed to more easily get through labor pain.
Digital is a New Normal
A health industry that has found itself fighting in the dark with the consequences of the pandemic will strongly need to adjust to big pressure due to increasing competition, new government regulations, rising costs, and customer demand for a higher quality of service.
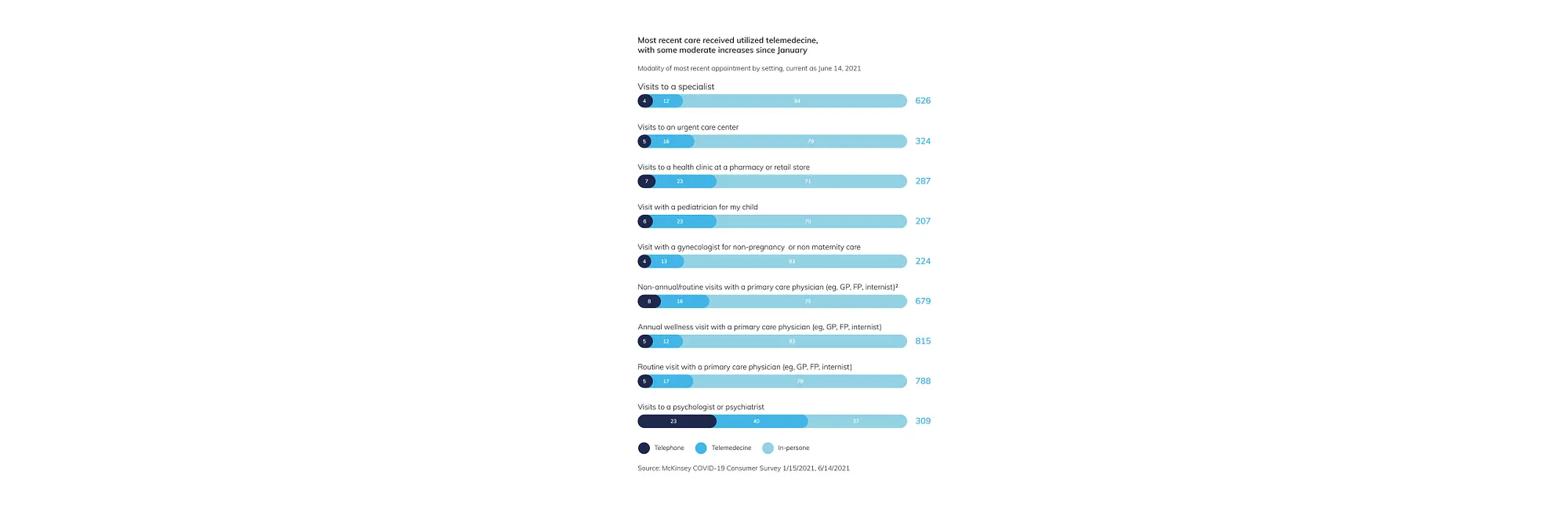
Such factors as security issues and data breaches, lack of patient confidentiality, and transparency will hamper the market growth. Though the healthcare deal activity will still remain robust as investors and executives will be looking to reposition themselves for post-pandemic growth.
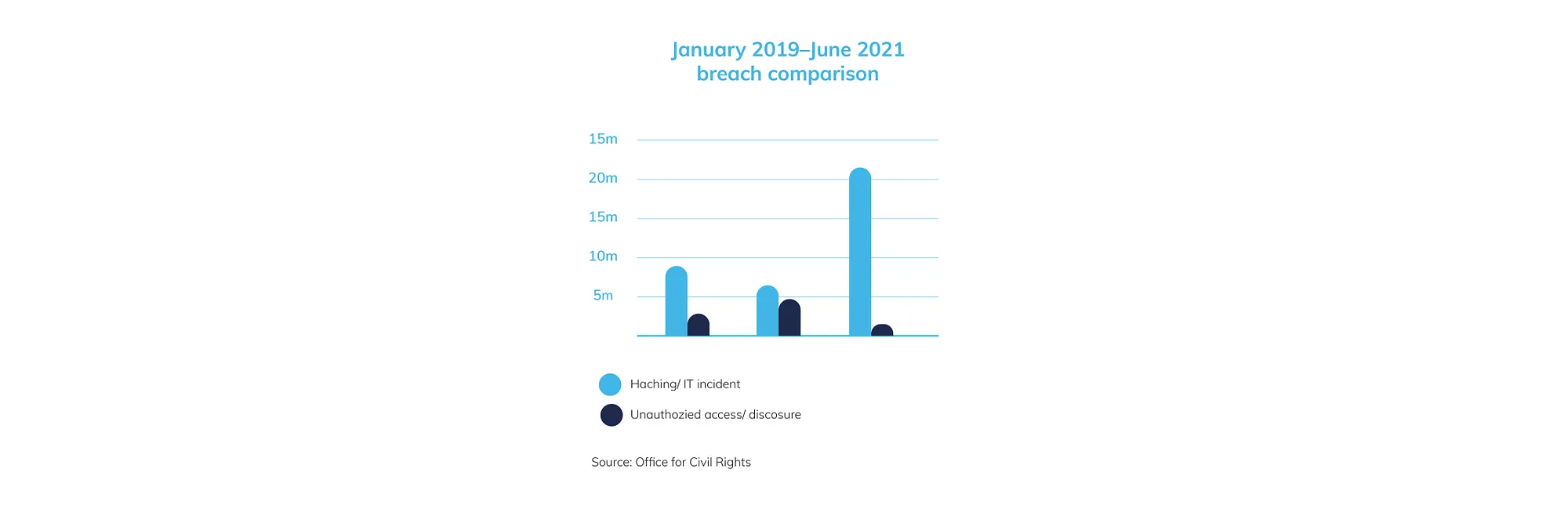
In 2022, the healthcare system will strongly need real-time insights to forecast the challenges and address them by being equipped with the latest technologies. The implementation of artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and VR&AR will play a crucial role in diagnostics, disease predictions, surgery preparation, and will significantly reduce expenses and improve the experience for both: patients and healthcare providers.
About inVerita
inVerita is a trusted technology partner to healthcare providers, offering a wide spectrum of consulting, design, engineering operations, and technology solutions. We engineer scalable health information exchange systems, cloud-based telehealth software, patient engagement solutions, EHR & EMR software, and support any kind of clinical software development specifically tailored to the requirements of your organization.