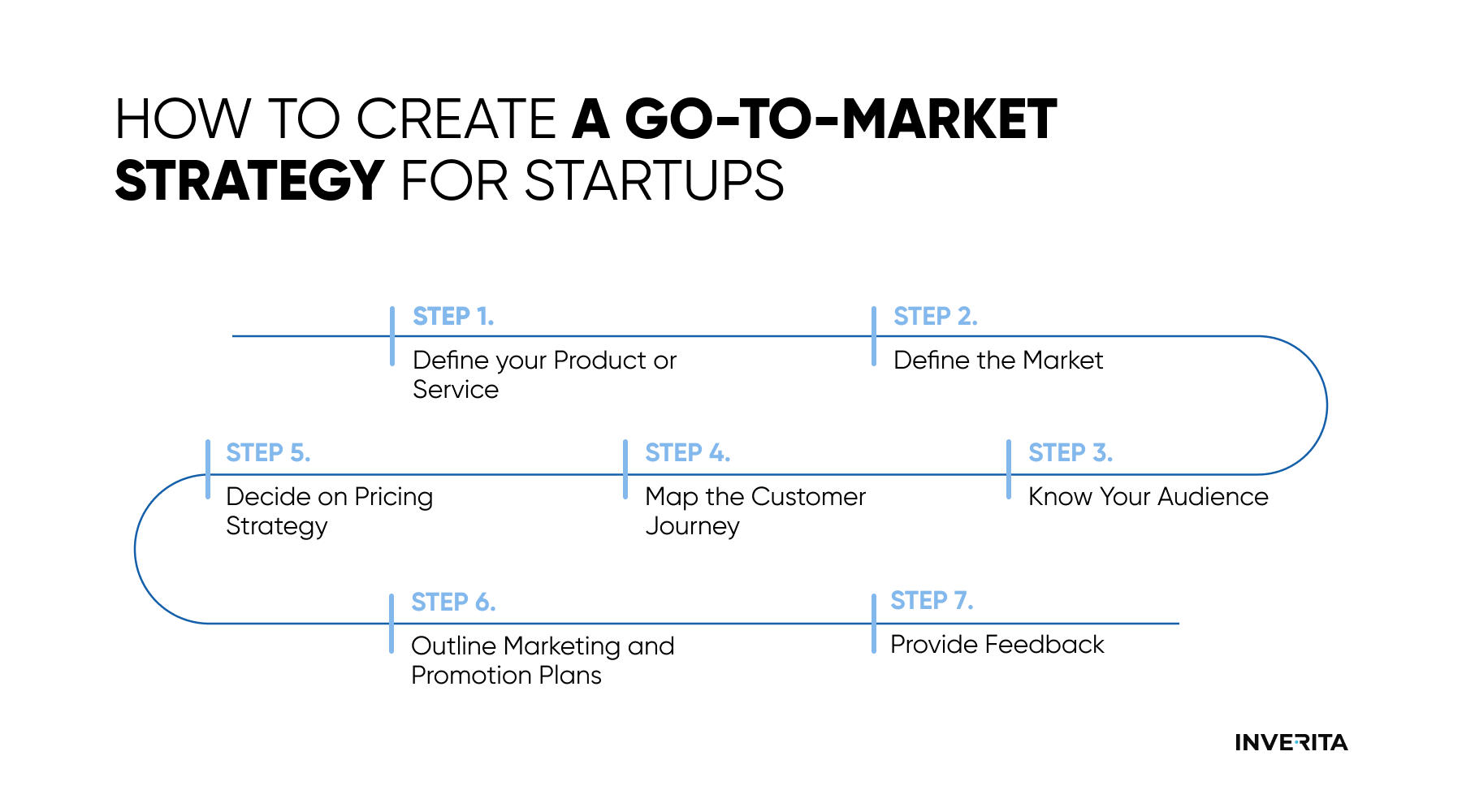
Step 1: Define your Product or Service
This may sound painfully obvious but you have to clearly define what is your product and what it does and what it does not before you dive into the next steps of your go-to-market strategy. Clarity brings scalability. You can start by answering these simple questions in writing:
- Who are your target customers?
- Who are your competitors or what are the alternatives to your product or service?
- What pain points is your product solving?
- What are your USPs?
- How is your product better than competitors’?
Step 2: Define the Market
Defining the market stage consists of several important elements.
Target Market
A target market is a specific group of people with shared characteristics that have been identified as the most likely customers of a product or service. A new product should meet a need or solve a problem that is most probably not universal. Therefore businesses should define a subset of customers that will use the product. Consumers are usually divided into four major segments: demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral.
For instance, Cle de Peau Beaute Synactif Soap is sold for $110 and is promoted as a product for rich and fashion-conscious customers who are willing to pay for a luxury product while a Dial soap costs around $5 on Amazon. Both products are on-demand but they cater to different target markets.
Total Addressable Market
The total addressable market shows how much potential for growing your startup has. Investors want to make sure that your product solves the existing problem in the market and they will get profit from that. The total addressable market asks a question: “How many people could potentially use the product or service?” to define the overall revenue opportunity that is available for your solution if 100% of the market share is achieved.
Market Needs
Market needs refer to the functional needs, desires, and interests of the target audience. Here you need to discover the drivers of demand for your product or service.
Market Test Results
The market test is an experiment held before the launch of a new product to find out if the product launch is going to be successful. The test is usually held in a small area with a small group of customers. If it succeeds, the product or service will be available to more customers or if not, the product will be dropped or improved and tested again.
Market testing brings the company two important benefits. First, the company gets a measure of its sales performance under typical market conditions. Second, managers can identify and solve any weaknesses. Despite these benefits, market testing isn’t a solution for each case as it’s a costly and laborious method.
Step 3: Know Your Audience
What are the interests of your target audience and what are their pain points? Where do they spend their time and which social media channels do they use? These are just a few of the questions you should figure out to understand if the target audience you are trying to reach is ready and willing to buy your product or service. Because if not, you are just losing time, money, and effort. So, how to analyze your audience?
- Define Target Market Demographics
Begin by categorizing your audience based on their demographics such as age, gender, income, job type, education, marital status, etc. Although some of these characteristics may seem irrelevant to you, they all work together to paint a picture that is essential for building an effective communication strategy.
- Understand Target Market Psychographics
Psychographics include behavioral patterns, preferences, and the attitude of your customers which you can understand by analyzing their activities, hobbies, preferred music, food, movies, etc. This information is quite subjective compared to demographics though it gives you a window into your audience’s personality.
- Identify the Challenges and Pain Points
By identifying each of the challenges and pain points your audience faces (financial/productivity/process/support, etc.), you can choose the right approach to overcome them and build an effective marketing strategy. The examples can be various: addressing customer pain points through landing pages, social ads, paid search ads, etc.
Customer pain points are highly subjective and even if you analyze two customers who face the same problem, the routes of this problem most probably would greatly differ from each other. The primary resources you can use for identifying these problems are the customers themselves, the sales team, and support.
Step 4: Map the Customer Journey
Customer journey mapping is a visual representation of a company's customer experience. Simply put, it shows all the stages that customers go through when interacting with your company from making a purchase online to leaving reviews on social media. Customer journey mapping provides an understanding of the path and channels customers take to get the products and forecasts the path of future customers as well.
There is no right or wrong way to create a customer journey map. Though it’s important to align your map with a chosen customer persona before you begin. Usually, the main stages of creating a customer journey map consist of such stages:
- Creating a Customer Persona - a fictional character that represents your average customer. We recommend starting with three personas at most to help in narrowing your character. Think about age, job, personality, etc. to try on the customers’ shoes.
- Deciding What to Measure - what goal you are trying to achieve with a current map? It’s also worth mentioning that the map is customizable and should evolve in correlation with your business needs.
- Organizing with Touchpoints and Measures - First of all, you need to identify touchpoints. A touch point is each moment when a customer interacts with your brand, for example, in advertisements. Secondly, break down the whole journey into stages based on the customer’s needs. You can use an Excel document to organize your map.
Step 5: Decide on Pricing Strategy
Determining your sales process is more than just picking numbers out of thin air. Deciding on your pricing strategy is a long and complicated process that involves in-depth knowledge of the product and marketplace. You should thoroughly analyze the pricing model of your competitors, how much it costs for you to ship and store your product, and so on. The investors also will be interested in the ways you are planning to market and promote your service.
Step 6: Outline Marketing and Promotion Plans
A marketing plan outlines a specific marketing strategy and shows how an organization is planning to use them and outreach to target specific buyer personas. A marketing plan includes such core elements as:
- Marketing Objectives: the objectives should be measurable and achievable;
- Current Marketing Positioning: the current state of the company’s marketing positioning;
- Market Research: the aforementioned in-depth analysis of market trends, customers’ needs, etc.
- Marketing Activities: a list of marketing actions scheduled for the period and their timelines;
- KPIs: to be tracked;
- Competition: study competitors and their strategies;
- Marketing Budget: allocation of financial resources to marketing activities.