Being one of the biggest breakthroughs of the past decade, blockchain technology has entered all walks of life: from manufacturing to fintech. It also has been among the most talked-about technologies of recent years with the global market size predicted to expand from $20.1 billion in 2024 to $249.9 billion in 2029.
Though technology is still in the process of evolving and its possibilities are actively being explored, it undoubtedly has already transformed many areas of business.
Distinguishing between actual blockchain-based applications and the hype surrounding them is one of the biggest challenges around blockchain. In this article, we will discuss real future trends of Blockchain technology to stay aware of. But, first of all, what’s Blockchain?
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a powerful technology that enables secure data sharing and access between multiple parties. It’s based on a mix of super-advanced cryptography and built-in incentives to remove the need for a centrally controlling third party and distribute power across all participants within its ecosystem. One of the key benefits of such a system for users and enterprises is gaining much more control and transparency over how their data is used. Now, let’s see what are the new trends in Blockchain.
Trend 1: Tokenization
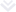
Tokenization is the process that involves the conversion of physical and non-physical assets on blockchain into digital tokens. Simply put, it's a digital representation of something that has value and contains sensitive information. This concept has gained a lot of popularity lately and many traditional financial enterprises have started leveraging the technology for the protection of confidential data.
For instance, the credit card numbers of users are replaced with a token that represents a string of non-sensitive numbers and letters. If criminals try to hack this information, they can find only a token without any credit card info. Tokenization is not limited to financial data, it’s also widely utilized by hospitals to securely handle patient records, by the government for voter registration, etc.
Blockchain tokenization revolves around assets, involving the creation of cryptocurrency tokens. It brings a high level of liquidity which significantly raises the number of potential customers in a wide range of industries.
Let’s take real estate as an example. A house with a two million tag has a quite limited circle of buyers. Though if it’s tokenized, anyone can buy a share that is affordable for them. There is no need for any intermediaries and paperwork, the transaction is fast, transparent, and secure.




_1764586939-small.webp)
